《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (7): 2233-2242.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023070918
高阳峄1,2, 雷涛1,2( ), 杜晓刚1, 李岁永3, 王营博1, 闵重丹1,2
), 杜晓刚1, 李岁永3, 王营博1, 闵重丹1,2
收稿日期:2023-07-11
修回日期:2023-09-18
接受日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-10-26
出版日期:2024-07-10
通讯作者:
雷涛
作者简介:高阳峄(1998—),男,陕西咸阳人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:图像处理、机器学习;基金资助:
Yangyi GAO1,2, Tao LEI1,2( ), Xiaogang DU1, Suiyong LI3, Yingbo WANG1, Chongdan MIN1,2
), Xiaogang DU1, Suiyong LI3, Yingbo WANG1, Chongdan MIN1,2
Received:2023-07-11
Revised:2023-09-18
Accepted:2023-09-20
Online:2023-10-26
Published:2024-07-10
Contact:
Tao LEI
About author:GAO Yangyi, born in 1998, M. S. candidate. His research interests include image processing, machine learning.Supported by:摘要:
基于卷积神经网络(CNN)获得回归密度图的方法已成为人群计数与定位的主流方法,但现有方法仍存在两个问题:首先传统方法获得的密度图在人群密集区域存在粘连和重叠问题,导致网络最终人群计数和定位错误;其次,常规卷积由于其权重不变,无法实现对图像特征的自适应提取,难以处理复杂背景和人群密度分布不均匀的图像。为解决上述问题,提出一种基于像素距离图(PDMap)和四维动态卷积网络(FDDCNet)的密集人群计数与定位方法。首先定义了一种新的PDMap,利用像素级标注点之间的空间距离关系,通过取反操作提高人头中心点周围像素的平滑度,避免人群密集区域的粘连重叠;其次,设计了一种FDDC模块,自适应地改变卷积四个维度的权重,提取不同视图提供的先验知识,应对复杂场景和分布不均匀导致的计数与定位困难,提高网络模型的泛化能力和鲁棒性;最后,采用阈值过滤局部不确定预测值,进一步提高计数与定位的准确性。在NWPU-Crowd数据集的测试集上:在人群计数方面,所提方法的平均绝对误差(MAE)和均方误差(MSE)分别为82.4和334.7,比MFP-Net(Multi-scale Feature Pyramid Network)分别降低了8.7%和26.9%;在人群定位方面,所提方法的综合评价指标F1值和精确率分别为71.2%和73.6%,比TopoCount(Topological Count)方法分别提升了3.0%和5.9%。实验结果表明,所提方法能够处理复杂背景的密集人群图像,取得了更高的计数准确率和定位精准度。
中图分类号:
高阳峄, 雷涛, 杜晓刚, 李岁永, 王营博, 闵重丹. 基于像素距离图和四维动态卷积网络的密集人群计数与定位方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(7): 2233-2242.
Yangyi GAO, Tao LEI, Xiaogang DU, Suiyong LI, Yingbo WANG, Chongdan MIN. Crowd counting and locating method based on pixel distance map and four-dimensional dynamic convolutional network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2024, 44(7): 2233-2242.
| 分辨率 | 阶段1 | 阶段2 | 阶段3 | 阶段4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 | 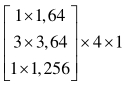 | 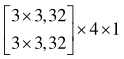 | 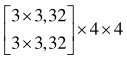 | 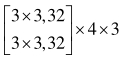 |
| 1/8 | 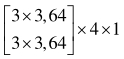 | 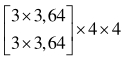 | 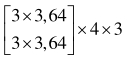 | |
| 1/16 | 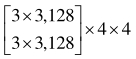 | 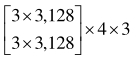 | ||
| 1/32 | 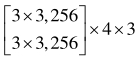 |
表1 高分辨率网络结构参数
Tab. 1 High-resolution network structure parameters
| 分辨率 | 阶段1 | 阶段2 | 阶段3 | 阶段4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 | 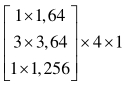 | 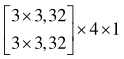 | 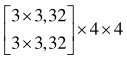 | 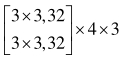 |
| 1/8 | 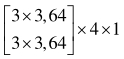 | 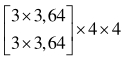 | 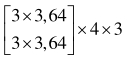 | |
| 1/16 | 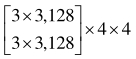 | 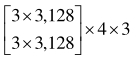 | ||
| 1/32 | 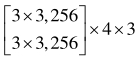 |
| 方法 | Shanghai Tech Part A | Shanghai Tech Part B | UCF-QRNF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | |
| MCNN[ | 110.2 | 173.2 | 26.4 | 41.3 | 277.0 | 426.0 |
| CSRNet[ | 68.2 | 115.0 | 10.6 | 16.0 | 121.3 | 208.0 |
| DADNet[ | 64.2 | 99.9 | 8.8 | 13.5 | 113.2 | 189.4 |
| SCAR[ | 66.3 | 114.1 | 9.5 | 15.2 | 132.6 | 177.4 |
| SFCN+[ | 64.8 | 107.5 | 7.6 | 13.0 | 114.5 | 193.6 |
| SUA-Fully[ | 66.9 | 125.6 | 12.3 | 17.9 | 119.2 | 213.3 |
| MFP-Net[ | 65.5 | 112.5 | 8.7 | 13.8 | 112.0 | 190.7 |
| NDConv[ | 61.4 | 104.2 | 7.8 | 13.8 | 91.2 | 165.6 |
| SC2Net[ | 58.9 | 97.7 | 6.9 | 11.4 | 98.5 | 174.5 |
| TransCrowd[ | 66.1 | 105.1 | 9.3 | 16.1 | 99.1 | 168.5 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 59.2 | 90.7 | 7.1 | 11.3 | 87.7 | 169.7 |
| DMCNet[ | 58.5 | 84.5 | 8.6 | 13.7 | 96.5 | 164.0 |
| CHS-Net[ | 59.2 | 97.8 | 7.1 | 11.2 | 83.4 | 144.9 |
| 本文方法 | 57.5 | 104.4 | 6.8 | 11.8 | 88.4 | 153.2 |
表2 不同方法在ShanghaiTech和UCF-QRNF数据集上的计数性能对比
Tab. 2 Comparison of counting performance on ShanghaiTech and UCF-QRNF datasets
| 方法 | Shanghai Tech Part A | Shanghai Tech Part B | UCF-QRNF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | |
| MCNN[ | 110.2 | 173.2 | 26.4 | 41.3 | 277.0 | 426.0 |
| CSRNet[ | 68.2 | 115.0 | 10.6 | 16.0 | 121.3 | 208.0 |
| DADNet[ | 64.2 | 99.9 | 8.8 | 13.5 | 113.2 | 189.4 |
| SCAR[ | 66.3 | 114.1 | 9.5 | 15.2 | 132.6 | 177.4 |
| SFCN+[ | 64.8 | 107.5 | 7.6 | 13.0 | 114.5 | 193.6 |
| SUA-Fully[ | 66.9 | 125.6 | 12.3 | 17.9 | 119.2 | 213.3 |
| MFP-Net[ | 65.5 | 112.5 | 8.7 | 13.8 | 112.0 | 190.7 |
| NDConv[ | 61.4 | 104.2 | 7.8 | 13.8 | 91.2 | 165.6 |
| SC2Net[ | 58.9 | 97.7 | 6.9 | 11.4 | 98.5 | 174.5 |
| TransCrowd[ | 66.1 | 105.1 | 9.3 | 16.1 | 99.1 | 168.5 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 59.2 | 90.7 | 7.1 | 11.3 | 87.7 | 169.7 |
| DMCNet[ | 58.5 | 84.5 | 8.6 | 13.7 | 96.5 | 164.0 |
| CHS-Net[ | 59.2 | 97.8 | 7.1 | 11.2 | 83.4 | 144.9 |
| 本文方法 | 57.5 | 104.4 | 6.8 | 11.8 | 88.4 | 153.2 |
| 方法 | Val | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | |
| MCNN[ | 218.5 | 700.6 | 232.5 | 714.6 |
| CSRNet[ | 104.8 | 433.8 | 190.6 | 491.4 |
| SCAR[ | 81.6 | 397.9 | 110.0 | 495.3 |
| SFCN+[ | 95.5 | 608.3 | 105.7 | 424.1 |
| DM-Count[ | — | — | 88.4 | 388.6 |
| SUA-Fully[ | 81.8 | 439.1 | 105.8 | 445.3 |
| SC2Net[ | — | — | 89.7 | 348.9 |
| MFP-Net[ | 84.2 | 434.4 | 90.3 | 458.0 |
| TransCrowd[ | 88.4 | 400.5 | 117.7 | 451.0 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 72.4 | 383.3 | 87.7 | 431.6 |
| MAN[ | — | — | 76.5 | 323.3 |
| CU-Count[ | — | — | 108.7 | 458.0 |
| 本文方法 | 62.7 | 259.1 | 82.4 | 334.7 |
表3 不同方法在NWPU-Crowd数据集上的计数性能对比
Tab. 3 Comparison counting performance on NWPU-Crowd datasets
| 方法 | Val | Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | MAE | MSE | |
| MCNN[ | 218.5 | 700.6 | 232.5 | 714.6 |
| CSRNet[ | 104.8 | 433.8 | 190.6 | 491.4 |
| SCAR[ | 81.6 | 397.9 | 110.0 | 495.3 |
| SFCN+[ | 95.5 | 608.3 | 105.7 | 424.1 |
| DM-Count[ | — | — | 88.4 | 388.6 |
| SUA-Fully[ | 81.8 | 439.1 | 105.8 | 445.3 |
| SC2Net[ | — | — | 89.7 | 348.9 |
| MFP-Net[ | 84.2 | 434.4 | 90.3 | 458.0 |
| TransCrowd[ | 88.4 | 400.5 | 117.7 | 451.0 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 72.4 | 383.3 | 87.7 | 431.6 |
| MAN[ | — | — | 76.5 | 323.3 |
| CU-Count[ | — | — | 108.7 | 458.0 |
| 本文方法 | 62.7 | 259.1 | 82.4 | 334.7 |

图6 所提方法在NWPU-Crowd数据集上的预测像素距离图、定位图和标注框图
Fig. 6 Prediction pixel distance maps, location maps and label block diagrams of proposed method on NWPU-Crowd dataset
| 方法 | Shanghai Tech Part A | Shanghai Tech Part B | UCF-QRNF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | |
| TFaces[ | 57.3 | 43.1 | 85.5 | 71.1 | 64.7 | 79.0 | 49.4 | 36.3 | 77.3 |
| RALoc[ | 69.2 | 61.3 | 79.5 | 68.0 | 60.0 | 78.3 | 53.3 | 59.4 | 48.3 |
| LSC[ | 68.0 | 69.6 | 66.5 | 71.2 | 71.7 | 70.6 | 58.2 | 58.6 | 57.7 |
| GL[ | — | — | — | — | — | — | 78.2 | 74.8 | 76.4 |
| CLTR[ | — | — | — | — | — | — | 82.2 | 79.7 | 80.9 |
| TopoCount[ | 74.6 | 72.7 | 73.6 | 75.3 | 74.6 | 73.7 | 81.8 | 79.0 | 80.3 |
| 本文方法 | 77.3 | 77.0 | 77.6 | 84.2 | 81.7 | 82.1 | 82.3 | 81.1 | 83.5 |
表4 不同方法在ShanghaiTech以及UCF-QRNF数据集上的定位性能对比 ( %)
Tab. 4 Comparison localing performance on ShanghaiTech and UCF-QRNF datasets
| 方法 | Shanghai Tech Part A | Shanghai Tech Part B | UCF-QRNF | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | |
| TFaces[ | 57.3 | 43.1 | 85.5 | 71.1 | 64.7 | 79.0 | 49.4 | 36.3 | 77.3 |
| RALoc[ | 69.2 | 61.3 | 79.5 | 68.0 | 60.0 | 78.3 | 53.3 | 59.4 | 48.3 |
| LSC[ | 68.0 | 69.6 | 66.5 | 71.2 | 71.7 | 70.6 | 58.2 | 58.6 | 57.7 |
| GL[ | — | — | — | — | — | — | 78.2 | 74.8 | 76.4 |
| CLTR[ | — | — | — | — | — | — | 82.2 | 79.7 | 80.9 |
| TopoCount[ | 74.6 | 72.7 | 73.6 | 75.3 | 74.6 | 73.7 | 81.8 | 79.0 | 80.3 |
| 本文方法 | 77.3 | 77.0 | 77.6 | 84.2 | 81.7 | 82.1 | 82.3 | 81.1 | 83.5 |
| 方法 | Val | Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | |
| Faster-RCNN[ | 7.3 | 96.4 | 3.8 | 6.7 | 95.8 | 3.5 |
| TFaces[ | 59.8 | 54.3 | 66.6 | 71.1 | 64.7 | 79.0 |
| RALoc[ | 62.5 | 69.2 | 56.9 | 68.0 | 60.0 | 78.3 |
| GL[ | — | — | — | 80.0 | 56.2 | 66.0 |
| CLTR[ | 73.9 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 69.4 | 67.6 | 68.5 |
| TopoCount[ | — | — | — | 69.1 | 69.5 | 68.7 |
| 本文方法 | 74.9 | 78.4 | 70.1 | 71.2 | 73.6 | 68.4 |
表5 不同方法在NWPU-Crowd数据集上的定位性能对比 ( %)
Tab. 5 Comparison localing performance on NWPU-Crowd dataset
| 方法 | Val | Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | F1 | 精确率 | 召回率 | |
| Faster-RCNN[ | 7.3 | 96.4 | 3.8 | 6.7 | 95.8 | 3.5 |
| TFaces[ | 59.8 | 54.3 | 66.6 | 71.1 | 64.7 | 79.0 |
| RALoc[ | 62.5 | 69.2 | 56.9 | 68.0 | 60.0 | 78.3 |
| GL[ | — | — | — | 80.0 | 56.2 | 66.0 |
| CLTR[ | 73.9 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 69.4 | 67.6 | 68.5 |
| TopoCount[ | — | — | — | 69.1 | 69.5 | 68.7 |
| 本文方法 | 74.9 | 78.4 | 70.1 | 71.2 | 73.6 | 68.4 |
| 方法 | 参数量/106 | 计算量/GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|
| CSRNet[ | 16.2 | 857.8 |
| TransCrowd[ | 86.8 | 49.3 |
| 本文方法 | 66.5 | 35.4 |
表6 不同方法的参数量和计算量对比
Tab. 6 Comparison of parameter and computational quautity of different methods
| 方法 | 参数量/106 | 计算量/GFLOPs |
|---|---|---|
| CSRNet[ | 16.2 | 857.8 |
| TransCrowd[ | 86.8 | 49.3 |
| 本文方法 | 66.5 | 35.4 |
| 方法 | 计数 | 定位 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | F1/% | |
| 高分辨率网络+Gaussian-Map | 59.6 | 108.1 | 71.1 |
| 高分辨率网络+PDMap | 57.5 | 103.4 | 77.0 |
表7 像素距离图消融实验结果
Tab. 7 Ablation experiment results of pixel distance map
| 方法 | 计数 | 定位 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | MSE | F1/% | |
| 高分辨率网络+Gaussian-Map | 59.6 | 108.1 | 71.1 |
| 高分辨率网络+PDMap | 57.5 | 103.4 | 77.0 |
| 方法 | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| CSRNet[ | 66.4 | 108.0 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 58.6 | 85.2 |
| 高分辨率网络 [ | 58.1 | 80.3 |
表8 高分辨率网络消融实验结果
Tab. 8 Ablation experiment results of high-resolution network
| 方法 | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| CSRNet[ | 66.4 | 108.0 |
| DLMP-Net[ | 58.6 | 85.2 |
| 高分辨率网络 [ | 58.1 | 80.3 |
| 方法 | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率网络-PDMap | 66.5 | 115.1 |
| +CondConv[ | 62.7 | 107.6 |
| +DyConv[ | 61.1 | 107.1 |
| +FDDC | 57.5 | 103.4 |
表9 四维动态卷积消融实验结果
Tab. 9 Ablation experiment results of four-dimensional dynamic convolution
| 方法 | MAE | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| 高分辨率网络-PDMap | 66.5 | 115.1 |
| +CondConv[ | 62.7 | 107.6 |
| +DyConv[ | 61.1 | 107.1 |
| +FDDC | 57.5 | 103.4 |
| 1 | FAN Z, ZhANG H, ZHANG Z, et al. A survey of crowd counting and density estimation based on convolutional neural network [J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 472: 224-251. |
| 2 | LEI Y, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Towards using count-level weak supervision for crowd counting [J]. Pattern Recognition, 2021, 109: 107616. |
| 3 | LI H, LIU L, YANG K, et al. Video crowd localization with multifocus Gaussian neighborhood attention and a large-scale benchmark [J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6032-6047. |
| 4 | YANG S, GUO W, REN Y. CrowdFormer: an overlap patching vision transformer for top-down crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. California: ijcai.org, 2022: 1545-1551. |
| 5 | ZHANG Y, CHOI S, HONG S. Spatio-channel attention blocks for cross-modal crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 16th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2022: 22-40. |
| 6 | ZHONG X, YAN Z, QIN J, et al. An improved normed-deformable convolution for crowd counting [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2022, 29: 1794-1798. |
| 7 | KHAN M A, MENOUAR H, HAMILA R. Revisiting crowd counting: state-of-the-art, trends, and future perspectives [J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2023, 129: 104597. |
| 8 | CHEN X, BIN Y, GAO C, et al. Relevant region prediction for crowd counting [J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 407: 399-408. |
| 9 | ZHANG Y, ZHOU D, CHEN S, et al. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network [C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 589-597. |
| 10 | LI Y, ZHANG X, CHEN D. CSRNet: dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes [C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1091-1100. |
| 11 | GUO D, LI K, ZHA Z-J, et al. DADNet: dilated-attention-deformable ConvNet for crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York: ACM, 2019: 1823-1832. |
| 12 | GAO J, WANG Q, YUAN Y. SCAR: spatial-/channel-wise attention regression networks for crowd counting [J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 363: 1-8. |
| 13 | LIANG D, CHEN X, XU W, et al. TransCrowd: weakly-supervised crowd counting with transformers [J]. SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences, 2022, 65: 1600104. |
| 14 | WANG Q, GAO J, LIN W, et al. Pixel-wise crowd understanding via synthetic data [J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129: 225-245. |
| 15 | WANG Q, GAO J, LIN W, et al. NWPU-Crowd: a large-scale benchmark for crowd counting and localization [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 43(6): 2141-2149. |
| 16 | CHEN Q, LEI T, GENG X, et al. DLMP-Net: a dynamic yet lightweight multi-pyramid network for crowd density estimation [C]// Proceedings of the 5th Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2022: 27-39. |
| 17 | IDREES H, TAYYAB M, ATHREY K, et al. Composition loss for counting, density map estimation and localization in dense crowds [C]// Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2018: 544-559. |
| 18 | ABOUSAMRA S, HOAI M, SAMARAS D, et al. Localization in the crowd with topological constraints [J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(2): 872-881. |
| 19 | LIU W, SALZMANN M, FUA P. Context-aware crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 5094-5103. |
| 20 | ZAND M, DAMIRCHI H, FARLEY A, et al. Multiscale crowd counting and localization by multitask point supervision [C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 1820-1824. |
| 21 | SONG Q, WANG C, JIANG Z, et al. Rethinking counting and localization in crowds: a purely point-based framework [C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 3345-3354. |
| 22 | LARADJI I H, ROSTAMZADEH N, PINHEIRO P O, et al. Where are the blobs: counting by localization with point supervision [C]// Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2018: 547-562. |
| 23 | LIU Y, SHI M, ZHAO Q, et al. Point in, box out: beyond counting persons in crowds [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 6462-6471. |
| 24 | GAO J, GONG M, LI X. Congested crowd instance localization with dilated convolutional Swin Transformer [J]. Neurocomputing, 2022, 513: 94-103. |
| 25 | SAM D B, PERI S V, SUNDARARAMAN M N, et al. Locate, size, and count: accurately resolving people in dense crowds via detection [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(8): 2739-2751. |
| 26 | YANG B, BENDER G, LE Q V, et al. CondConv: conditionally parameterized convolutions for efficient inference [C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 1307-1318. |
| 27 | CHEN Y, DAI X, LIU M, et al. Dynamic convolution: attention over convolution kernels [C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 11027-11036. |
| 28 | ZHANG Y, ZHANG J, WANG Q, et al. DyNet: dynamic convolution for accelerating convolutional neural networks [EB/OL]. [2023-07-01]. . |
| 29 | OLMSCHENK G, TANG H, ZHU Z. Improving dense crowd counting convolutional neural networks using inverse k-nearest neighbor maps and multiscale upsampling [EB/OL]. [2023-07-01]. . |
| 30 | SUN K, XIAO B, LIU D, et al. Deep high-resolution representation learning for human pose estimation [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 5686-5796. |
| 31 | HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition [C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| 32 | DAI M, HUANG Z, GAO J, et al. Cross-head supervision for crowd counting with noisy annotations [C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2023: 1-5. |
| 33 | WANG M, CAI H, DAI Y, et al. Dynamic mixture of counter network for location-agnostic crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2023: 167-177. |
| 34 | LIN H, MA Z, JI R, et al. Boosting crowd counting via multifaceted attention [C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 19596-19605. |
| 35 | LI C, HU X, ABOUSAMRA S, et al. Calibrating uncertainty for semi-supervised crowd counting [EB/OL]. [2023-07-01]. . |
| 36 | MENG Y, ZHANG H, ZHAO Y, et al. Spatial uncertainty-aware semi-supervised crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 15529-15539. |
| 37 | LEI T, ZHANG D, WANG R, et al. MFP-Net: multi-scale feature pyramid network for crowd counting [J]. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(14): 3522-3533. |
| 38 | LIANG L, ZHAO H, ZHOU F, et al. SC2Net: scale-aware crowd counting network with pyramid dilated convolution [J]. Applied Intelligence, 2023, 53: 5146-5159. |
| 39 | WANG B, LIU H, SAMARAS D, et al. Distribution matching for crowd counting [C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2020: 1595-1607. |
| 40 | HU P, RAMANAN D. Finding tiny faces [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 1522-1530. |
| 41 | LIANG D, XU W, BAI X. An end-to-end transformer model for crowd localization [C]// Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2022: 38-54. |
| 42 | LIU C, WENG X, MU Y. Recurrent attentive zooming for joint crowd counting and precise localization [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 1217-1226. |
| 43 | REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks [C]// Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2015: 91-99. |
| 44 | WAN J, LIU Z, CHAN A B. A generalized loss function for crowd counting and localization [C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 1974-1983. |
| [1] | 李云, 王富铕, 井佩光, 王粟, 肖澳. 基于不确定度感知的帧关联短视频事件检测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2903-2910. |
| [2] | 赵志强, 马培红, 黑新宏. 基于双重注意力机制的人群计数方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2886-2892. |
| [3] | 秦璟, 秦志光, 李发礼, 彭悦恒. 基于概率稀疏自注意力神经网络的重性抑郁疾患诊断[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2970-2974. |
| [4] | 陈虹, 齐兵, 金海波, 武聪, 张立昂. 融合1D-CNN与BiGRU的类不平衡流量异常检测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2493-2499. |
| [5] | 赵宇博, 张丽萍, 闫盛, 侯敏, 高茂. 基于改进分段卷积神经网络和知识蒸馏的学科知识实体间关系抽取[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2421-2429. |
| [6] | 张春雪, 仇丽青, 孙承爱, 荆彩霞. 基于两阶段动态兴趣识别的购买行为预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2365-2371. |
| [7] | 孙逊, 冯睿锋, 陈彦如. 基于深度与实例分割融合的单目3D目标检测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2208-2215. |
| [8] | 王东炜, 刘柏辰, 韩志, 王艳美, 唐延东. 基于低秩分解和向量量化的深度网络压缩方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 1987-1994. |
| [9] | 李伟, 张晓蓉, 陈鹏, 李清, 张长青. 基于正态逆伽马分布的多尺度融合人群计数算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2243-2249. |
| [10] | 沈君凤, 周星辰, 汤灿. 基于改进的提示学习方法的双通道情感分析模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1796-1806. |
| [11] | 黄梦源, 常侃, 凌铭阳, 韦新杰, 覃团发. 基于层间引导的低光照图像渐进增强算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1911-1919. |
| [12] | 李健京, 李贯峰, 秦飞舟, 李卫军. 基于不确定知识图谱嵌入的多关系近似推理模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1751-1759. |
| [13] | 姚迅, 秦忠正, 杨捷. 生成式标签对抗的文本分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1781-1785. |
| [14] | 孙敏, 成倩, 丁希宁. 基于CBAM-CGRU-SVM的Android恶意软件检测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(5): 1539-1545. |
| [15] | 高文烁, 陈晓云. 基于节点结构的点云分类网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(5): 1471-1478. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||