《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (9): 2885-2896.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022081237
所属专题: 网络与通信
万义程1, 杨光祥1,2( ), 张庆达1, 甘晨阳1, 易林1
), 张庆达1, 甘晨阳1, 易林1
收稿日期:2022-08-22
修回日期:2022-10-23
接受日期:2022-11-03
发布日期:2023-01-11
出版日期:2023-09-10
通讯作者:
杨光祥
作者简介:万义程(1996—),男,江西南昌人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:LoRaWAN、物联网、无线通信基金资助:
Yicheng WAN1, Guangxiang YANG1,2( ), Qingda ZHANG1, Chenyang GAN1, Lin YI1
), Qingda ZHANG1, Chenyang GAN1, Lin YI1
Received:2022-08-22
Revised:2022-10-23
Accepted:2022-11-03
Online:2023-01-11
Published:2023-09-10
Contact:
Guangxiang YANG
About author:WAN Yicheng, born in 1996, M. S. candidate. His research interests include LoRaWAN, internet of things, wireless communication.Supported by:摘要:
LoRaWAN是低功耗广域网(LPWAN)中的一种无线通信标准,为物联网的发展提供了支撑。然而,受限于扩频因子(SF)间不完全正交性的特点和LoRaWAN不具备先听后发(LBT)机制的事实,基于ALOHA的传输调度方式会引发严重的信道冲突,极大降低了LoRa(Long Range Radio)网络的扩展性。为提高LoRa网络的扩展性,提出用非坚持型载波监听多路访问(NP-CSMA)机制替代LoRaWAN中ALOHA的介质访问控制机制,通过LBT协调LoRa网络中SF相同的各个节点接入信道的时间。不同SF之间的传输则采用多种SF信号并行传输,以减少共信道中同SF干扰和避免SF间干扰。为了分析NP-CSMA对LoRa网络扩展性的影响,通过理论分析和NS3仿真对LoRaWAN与NP-CSMA构建的LoRa网络进行比较。实验结果表明,在相同的条件下,与LoRaWAN相比,NP-CSMA在网络通信负载率为1的情况下,它的理论数据包交付率(PDR)性能比LoRaWAN高58.09%。在信道利用率方面,与LoRaWAN相比,NP-CSMA的饱和信道利用率提高了214.9%,容纳的节点数量也增加了60.0%。另外,NP-CSMA的平均时延在网络通信负载率小于1.7时也低于确认型LoRaWAN,而且在扩频因子为7和10时,它用于维持信道活动检测(CAD)模式所造成的额外能耗也比LoRaWAN用于接收来自网关确认消息所需的额外能耗低1.0~1.3 mJ和2.5~5.1 mJ;充分反映了NP-CSMA可以有效提高LoRa网络的可扩展性。
中图分类号:
万义程, 杨光祥, 张庆达, 甘晨阳, 易林. 非坚持型载波监听多路访问机制对LoRa网络扩展性的影响[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(9): 2885-2896.
Yicheng WAN, Guangxiang YANG, Qingda ZHANG, Chenyang GAN, Lin YI. Impact of non-persistent carrier sense multiple access mechanism on scalability of LoRa networks[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(9): 2885-2896.
| SF | SNR/dB | SF | SNR/dB | SF | SNR/dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | -7.0 | 9 | -12.5 | 11 | -18.5 |
| 8 | -10.0 | 10 | -15.0 | 12 | -21.0 |
表1 BER为10-4时不同SF对应的SNR阈值
Tab. 1 SNR thresholds corresponding to different SF when BER is 10-4
| SF | SNR/dB | SF | SNR/dB | SF | SNR/dB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | -7.0 | 9 | -12.5 | 11 | -18.5 |
| 8 | -10.0 | 10 | -15.0 | 12 | -21.0 |

图5 基于up-chirp,由K=150的参考信号和K=50,100的干扰信号重叠组成的LoRa信号
Fig. 5 Based on up-chirp, LoRa signal composed of a reference signal with K=150 and interference signals with K=50,100

图6 SIR=-20 dB的条件下,K=150的参考信号和K=50,100的干扰信号重叠组成的LoRa信号解线性调频后的FFT输出
Fig. 6 At SIR=-20 dB, FFT output of LoRa signal composed of a reference signal with K=150 and interfering signals with K=50,100
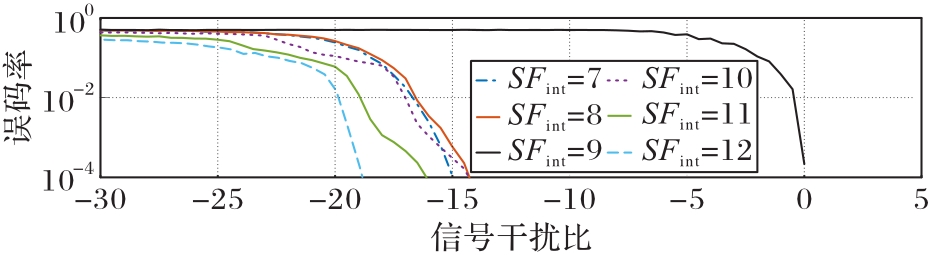
图7 不同SFint的干扰信号的组合下,SF=9的参考信号的BER与SIR之间的关系
Fig. 7 Relationship between BER and SIR of reference signal with SF=9 under combinations of interference signals with different SFint
| SFref | SFint不同时所需的SIR阈值/dB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFint=7 | SFint=8 | SFint=9 | SFint=10 | SFint=11 | SFint=12 | |
| 7 | 0.0 | -10.0 | -12.0 | -13.0 | -13.5 | -13.5 |
| 8 | -12.5 | 0.0 | -13.0 | -15.0 | -15.5 | -16.0 |
| 9 | -15.5 | -15.5 | 0.0 | -16.0 | -17.5 | -19.5 |
| 10 | -18.0 | -18.0 | -18.0 | 0.0 | -18.5 | -20.5 |
| 11 | -20.5 | -20.5 | -21.0 | -21.0 | 0.0 | -22.0 |
| 12 | -23.5 | -23.5 | -24.0 | -25.0 | -25.0 | 0.0 |
表2 BER为10-3的条件下,多种SF组合信号中参考信号解调所需的SIR阈值
Tab. 2 SIR thresholds required for demodulation of reference signals in combined signals of multiple SF when BER is 10-3
| SFref | SFint不同时所需的SIR阈值/dB | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SFint=7 | SFint=8 | SFint=9 | SFint=10 | SFint=11 | SFint=12 | |
| 7 | 0.0 | -10.0 | -12.0 | -13.0 | -13.5 | -13.5 |
| 8 | -12.5 | 0.0 | -13.0 | -15.0 | -15.5 | -16.0 |
| 9 | -15.5 | -15.5 | 0.0 | -16.0 | -17.5 | -19.5 |
| 10 | -18.0 | -18.0 | -18.0 | 0.0 | -18.5 | -20.5 |
| 11 | -20.5 | -20.5 | -21.0 | -21.0 | 0.0 | -22.0 |
| 12 | -23.5 | -23.5 | -24.0 | -25.0 | -25.0 | 0.0 |
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 节点散落半径范围 | 0~2 000 m 随机散落 |
| 节点数 | 0~400 |
| 频段 | 470 MHz |
| 编码速率 | 4/5 |
| 带宽 | 125 kHz |
| 传播损耗模型 | Okumura-Hata 模型 |
| 前导码 | 8个符号 |
| LoRa数据帧FHDR字段 | 7 B |
| MAC层负载大小 | 30/50 B |
| 空中传输时间(Tdata) | 式(14) |
| 网关模块 | SX1301 |
| 网关天线高度 | 15 m |
| 节点模块 | SX1272 |
| 节点天线高度 | 1 m |
| 电压 | 3.3 V |
| 发送功率 | 92.4 mW |
| 睡眠功率 | 4.95 μW |
| 侦听功率 | 4.62 mW |
| 接收功率 | 36.96 mW |
表3 基本仿真参数
Tab. 3 Basic simulation parameters
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 节点散落半径范围 | 0~2 000 m 随机散落 |
| 节点数 | 0~400 |
| 频段 | 470 MHz |
| 编码速率 | 4/5 |
| 带宽 | 125 kHz |
| 传播损耗模型 | Okumura-Hata 模型 |
| 前导码 | 8个符号 |
| LoRa数据帧FHDR字段 | 7 B |
| MAC层负载大小 | 30/50 B |
| 空中传输时间(Tdata) | 式(14) |
| 网关模块 | SX1301 |
| 网关天线高度 | 15 m |
| 节点模块 | SX1272 |
| 节点天线高度 | 1 m |
| 电压 | 3.3 V |
| 发送功率 | 92.4 mW |
| 睡眠功率 | 4.95 μW |
| 侦听功率 | 4.62 mW |
| 接收功率 | 36.96 mW |
| 参数 | LoRaWAN | NP-CSMA |
|---|---|---|
| 扩频因子 | 7,10 | 7,10 |
| 信道 | 1个占空比为1%的上行信道和1个占空比为10%的下行信道 | 1个占空比为1%的上行信道和1个占空比为10%的下行信道 |
| 重传次数 | 8 | 4 |
| CAD功率 | — | 接收功率(1.4 mA) |
| CAD持续时间TCAD | — | 取决于SF[ |
| 退避时间 | — | 基于式(13) |
| 数据周期 | 100Tdata | 100Tdata |
表4 LoRaWAN和NP-CSMA仿真实验参数
Tab. 4 LoRaWAN and NP-CSMA simulation experimental parameters
| 参数 | LoRaWAN | NP-CSMA |
|---|---|---|
| 扩频因子 | 7,10 | 7,10 |
| 信道 | 1个占空比为1%的上行信道和1个占空比为10%的下行信道 | 1个占空比为1%的上行信道和1个占空比为10%的下行信道 |
| 重传次数 | 8 | 4 |
| CAD功率 | — | 接收功率(1.4 mA) |
| CAD持续时间TCAD | — | 取决于SF[ |
| 退避时间 | — | 基于式(13) |
| 数据周期 | 100Tdata | 100Tdata |

图11 随着终端节点数量的增加,在单信道和MACPayload=50 B的情况下,LoRaWAN、NP-CSMA在SF=7,10下的PDR
Fig. 11 With increase of node number, PDR of LoRaWAN, NP-CSMA with SF=7,10 under conditions of single channel and MACPayload =50 B

图12 随着终端节点数量的增加,在单信道和MACPayload=50 B的情况下,LoRaWAN、NP-CSMA在SF=7,10下的信道利用率
Fig. 12 With increase of node number, channel utilization of LoRaWAN, NP-CSMA with SF=7,10 under conditions of single channel and MACPayload=50 B
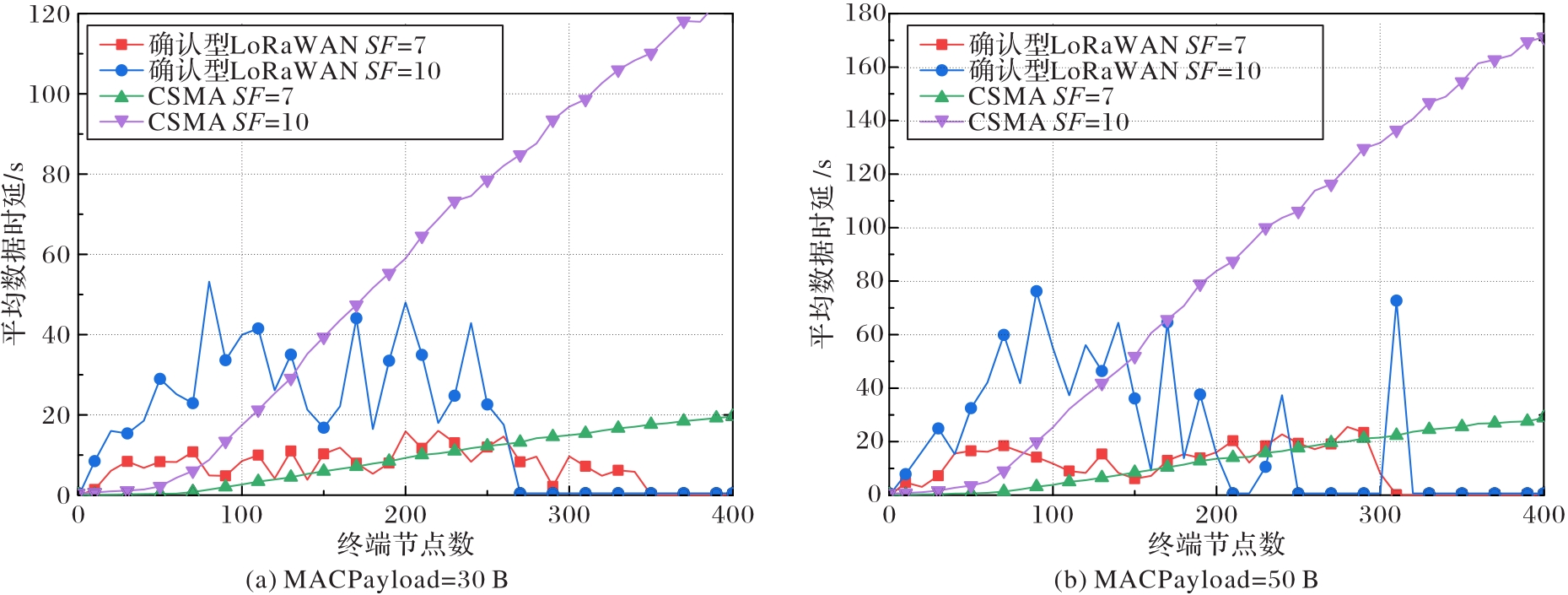
图13 基于MACPayload=30,50 B两种数据包负载长度,确认型LoRaWAN和NP-CSMA在SF=7,10下的平均时延
Fig. 13 Average latency of confirmed LoRaWAN and NP-CSMA with SF=7,10 based on two packet load lengths of MACPayload=30,50 B

图 14 LoRaWAN、NP-CSMA的终端节点在SF=7和10下发送一个MACPayload=50 B的数据包所需的平均能耗
Fig. 14 Average energy consumption of a single packet with MACPayload=50 B sent by terminal node of LoRaWAN,NP-CSMA at SF=7,10
| 1 | ČOLAKOVIĆ A, HADŽIALIĆ M. Internet of Things (IoT): a review of enabling technologies, challenges, and open research issues[J]. Computer Networks, 2018, 144: 17-39. 10.1016/j.comnet.2018.07.017 |
| 2 | MAGRIN D. Network level performances of a LoRa system[D]. Parva: Università degli Studi di Padova, 2016: 1-80. |
| 3 | QUERALTA J P, GIA T N, ZOU Z, et al. Comparative study of LPWAN technologies on unlicensed bands for M2M communication in the IoT: beyond LoRa and LoRaWAN[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2019, 155: 343-350. 10.1016/j.procs.2019.08.049 |
| 4 | MROUE H, NASSER A, HAMRIOUI S, et al. MAC layer-based evaluation of IoT technologies: LoRa, SigFox and NB-IoT[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Middle East and North Africa Communications Conference. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. 10.1109/menacomm.2018.8371016 |
| 5 | LAVRIC A, POPA V. LoRa wide-area networks from an Internet of Things perspective[C]// Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 1-4. 10.1109/ecai.2017.8166397 |
| 6 | GOURSAUD C, GORCE J M. Dedicated networks for IoT: PHY / MAC state of the art and challenges[J]. EAI Endorsed Transactions on Internet of Things, 2015, 1(1): No.e3. 10.4108/eai.26-10-2015.150597 |
| 7 | 刘树聃,孙继炫. LoRa调制技术及解调算法[J]. 电讯技术, 2018, 58(12): 1447-1451. 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2018.12.014 |
| LIU S D, SUN J X. LoRa modulation technology and demodulation algorithm[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2018, 58(12): 1447-1451. 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893x.2018.12.014 | |
| 8 | Corporation Semtech. Understanding the LoRa adaptive data rate[EB/OL]. (2019-12) [2022-08-10].. |
| 9 | MROUE H, PARREIN B, HAMRIOUI S, et al. LoRa+: an extension of LoRaWAN protocol to reduce infrastructure costs by improving the Quality of Service[J]. Internet of Things, 2020, 9: No.100176. 10.1016/j.iot.2020.100176 |
| 10 | Corporation Semtech. LoRa and LoRaWAN: a technical overview[EB/OL]. (2019-12) [2022-08-15].. 10.1201/9781003042600-16 |
| 11 | Alliance Lora. Homepage of Lora Alliance[EB/OL]. [2022-08-15].. |
| 12 | F van den ABEELE, HAXHIBEQIRI J, MOERMAN I, et al. Scalability analysis of large-scale LoRaWAN networks in ns-3[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(6): 2186-2198. 10.1109/jiot.2017.2768498 |
| 13 | DE SOUZA SANT’ANA J M, HOELLER A, SOUZA R D, et al. LoRa performance analysis with superposed signal decoding[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(11) : 1865-1868. 10.1109/lwc.2020.3006588 |
| 14 | ZHANG C W, WANG L K, JIAO L B, et al. A novel orthogonal LoRa multiple access algorithm for satellite Internet of Things[J]. China Communications, 2022, 19(3): 279-289. 10.23919/jcc.2022.03.020 |
| 15 | CROCE D, GUCCIARDO M, TINNIRELLO I, et al. Impact of spreading factor imperfect orthogonality in LoRa communications[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 International Tyrrhenian Workshop on Digital Communication, CCIS 766. Cham: Springer, 2017: 165-179. 10.1007/978-3-319-67639-5_13 |
| 16 | CROCE D, GUCCIARDO M, MANGIONE S, et al. Impact of LoRa imperfect orthogonality: analysis of link-level performance[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(4): 796-799. 10.1109/lcomm.2018.2797057 |
| 17 | MAHMOOD A, SISINNI E, GUNTUPALLI L, et al. Scalability analysis of a LoRa network under imperfect orthogonality[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2019, 15(3): 1425-1436. 10.1109/tii.2018.2864681 |
| 18 | WARET A, KANEKO M, GUITTON A, et al. LoRa throughput analysis with imperfect spreading factor orthogonality[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(2): 408-411. 10.1109/lwc.2018.2873705 |
| 19 | BELTRAMELLI L, MAHMOOD A, ÖSTERBERG P, et al. LoRa beyond ALOHA: an investigation of alternative random access protocols[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(5): 3544-3554. 10.1109/tii.2020.2977046 |
| 20 | TO T H, DUDA A. Simulation of LoRa in NS-3: improving LoRa performance with CSMA[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1-7. 10.1109/icc.2018.8422800 |
| 21 | PHAM C. Investigating and experimenting CSMA channel access mechanisms for LoRa IoT networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1-6. 10.1109/wcnc.2018.8376997 |
| 22 | 孙楠. 基于分数傅里叶变换的LoRa调制与解调研究[D]. 哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学, 2019: 7-16. |
| SUN N. Research on LoRa modulation and demodulation based on fractional Fourier transform[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019: 7-16. | |
| 23 | TAPPAREL J, AFISIADIS O, MAYORAZ P, et al. An open-source LoRa physical layer prototype on GNU radio[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE 21st International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 1-5. 10.1109/spawc48557.2020.9154273 |
| 24 | TAPPAREL J, XHONNEUX M, BOL D, et al. Enhancing the reliability of dense LoRaWAN networks with multi-user receivers[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2021, 2: 2725-2738. 10.1109/ojcoms.2021.3134091 |
| 25 | 谢希仁. 计算机网络[M]. 第七版. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2017: 397-406. |
| XIE X R. Computer Networks[M]. 7th ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2017: 397-406. | |
| 26 | Alliance LoRa. TS001-1.0.4 LoRaWAN L2 1.0.4 specification [S/OL]. [2022-08-17]. |
| specifications/t s001-1-0-4-lorawan-l2-1-0-4 -specification. | |
| 27 | Alliance LoRa. RP002-1.0.2 LoRaWAN regional parameters [S/OL]. [2022-08-18].. |
| 28 | Corporation Semtech. AN 1200.21: reading channel RSSI during a CAD[EB/OL]. (2014-10) [2022-08-18].. |
| 29 | KLEINROCK L, TOBAGI F. Packet switching in radio channels: part I - carrier sense multiple-access modes and their throughput-delay characteristics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 1975, 23(12): 1400-1416. 10.1109/tcom.1975.1092768 |
| 30 | RIVERO-ANGELES M E, LARA-RODRÍGUEZ D, CRUZ-PÉREZ F A. Random-access control mechanisms using adaptive traffic load in ALOHA and CSMA strategies for EDGE[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2005, 54(3): 1160-1186. 10.1109/tvt.2005.844657 |
| 31 | 韩泽军,丁洪伟,保利勇,等. 无线Ad Hoc网络中新型N-CSMA协议采用多优先级时的性能分析[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 42(1): 43-49. 10.1504/ijcnds.2020.108163 |
| HAN Z J, DING H W, BAO L Y, et al. Performance analysis of new N-CSMA protocol in wireless Ad Hoc networks with multi-priority[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Sciences Edition), 2020, 42(1): 43-49. 10.1504/ijcnds.2020.108163 | |
| 32 | WONG P K, YIN D J, LEE T T. Analysis of non-persistent CSMA protocols with exponential backoff scheduling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2011, 59(8): 2206-2214. 10.1109/tcomm.2011.051811.100241 |
| 33 | HOU Y J, LIU Z J, SUN D C. A novel MAC protocol exploiting concurrent transmissions for massive LoRa connectivity[J]. Journal of Communications and Networks, 2020, 22(2): 108-117. 10.1109/jcn.2020.000005 |
| [1] | 花敏, 魏佳楠, 赵伟, 孟硕. LoRa信号干扰分析与性能研究[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2848-2854. |
| [2] | 李皎, 张秀山, 宁远航. 降低跨分片交易比例的区块链分片方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1889-1896. |
| [3] | 陈姿芊, 牛科迪, 姚中原, 斯雪明. 适用于物联网的区块链轻量化技术综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(12): 3688-3698. |
| [4] | 牛科迪, 李敏, 姚中原, 斯雪明. 面向物联网的区块链共识算法综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(12): 3678-3687. |
| [5] | 孙栋, 王彪, 徐云. 基于RDMA的区块传输机制设计与实现[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(2): 484-489. |
| [6] | 门瑞, 樊书嘉, 阿喜达, 杜邵昱, 樊秀梅. 物联网中结合计算卸载和区块链的综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(10): 3008-3016. |
| [7] | 孙源, 沈文建, 倪朋勃, 毛敏, 谢雅琪, 徐朝农. 实时工业物联网的功率域非正交多址接入基站选址算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(1): 209-214. |
| [8] | 王旭, 申玉民, 熊晓芸, 李鹏, 王金龙. 基于哈希图的建筑物联网数据管理方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(8): 2471-2480. |
| [9] | 罗鸿秋, 胡圣波. 面向物联网的近地轨道超大规模卫星星座数据命名机制[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(7): 2146-2154. |
| [10] | 张杰, 许姗姗, 袁凌云. 基于区块链与边缘计算的物联网访问控制模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(7): 2104-2111. |
| [11] | 董宁, 程晓荣, 张铭泉. 基于物联网平台的动态权重损失函数入侵检测系统[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(7): 2118-2124. |
| [12] | 刘晶, 董志红, 张喆语, 孙志刚, 季海鹏. 基于联邦增量学习的工业物联网数据共享方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(4): 1235-1243. |
| [13] | 郑鑫, 李素月, 王安红, 李美玲, MUHAIDAT Sami, 宁爱平. 协作多输入多输出环境反向散射通信系统遍历速率分析[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(3): 974-979. |
| [14] | 卿欣艺, 陈玉玲, 周正强, 涂园超, 李涛. 基于中国剩余定理的区块链存储扩展模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(7): 1977-1982. |
| [15] | 张鲁飞, 孙茹君, 秦芳. 面向图计算的运行时系统的消息聚合技术[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(4): 984-989. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||