《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (9): 2692-2699.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022091405
• 2022第10届CCF大数据学术会议 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2022-09-19
修回日期:2022-10-18
接受日期:2022-10-21
发布日期:2023-09-10
出版日期:2023-09-10
通讯作者:
钱清
作者简介:王宏(1995—),男,四川南充人,硕士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向:人工智能、图像被动取证基金资助:
Hong WANG, Qing QIAN( ), Huan WANG, Yong LONG
), Huan WANG, Yong LONG
Received:2022-09-19
Revised:2022-10-18
Accepted:2022-10-21
Online:2023-09-10
Published:2023-09-10
Contact:
Qing QIAN
About author:WANG Hong, born in 1995, M. S. candidate. His research interests include artificial intelligence, passive image forensics.Supported by:摘要:
卷积神经网络(CNN)因辨识度高、易于理解、可学习性强而被用于图像取证,但它固有的感受野增加缓慢、忽略长端依赖性、计算量庞大等缺点导致深度学习算法的精度与轻量化部署效果并不理想,不适用于以轻量化形式实现图像篡改定位的场景。为解决上述问题,提出一种基于轻量化网络的图像复制-粘贴篡改检测算法——LKA-EfficientNet(Large Kernel Attention EfficientNet)。LKA-EfficientNet具有长端依赖性和全局感受野的特性,且优化了EfficientNetV2的参数量,提高了图像篡改定位速度和精度。首先,将输入图像通过基于大核注意力(LKA)卷积的基干网络进行处理,得到候选特征图;随后,使用不同尺寸的特征图构建特征金字塔进行特征匹配;最后,将特征匹配后的特征图进行融合以定位图像篡改区域;此外,LKA-EfficientNet使用三元组交叉熵损失函数进一步提升了算法定位篡改图像的精度。实验结果表明,LKA-EfficientNet与同类型的Dense-InceptionNet算法相比,不仅能够降低29.54%的浮点运算量,而且F1分数也提高了4.88%,验证了LKA-EfficientNet可以在保持高检测性能的同时降低计算量。
中图分类号:
王宏, 钱清, 王欢, 龙永. 融合大核注意力卷积的轻量化图像篡改定位算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(9): 2692-2699.
Hong WANG, Qing QIAN, Huan WANG, Yong LONG. Lightweight image tamper localization algorithm based on large kernel attention convolution[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(9): 2692-2699.
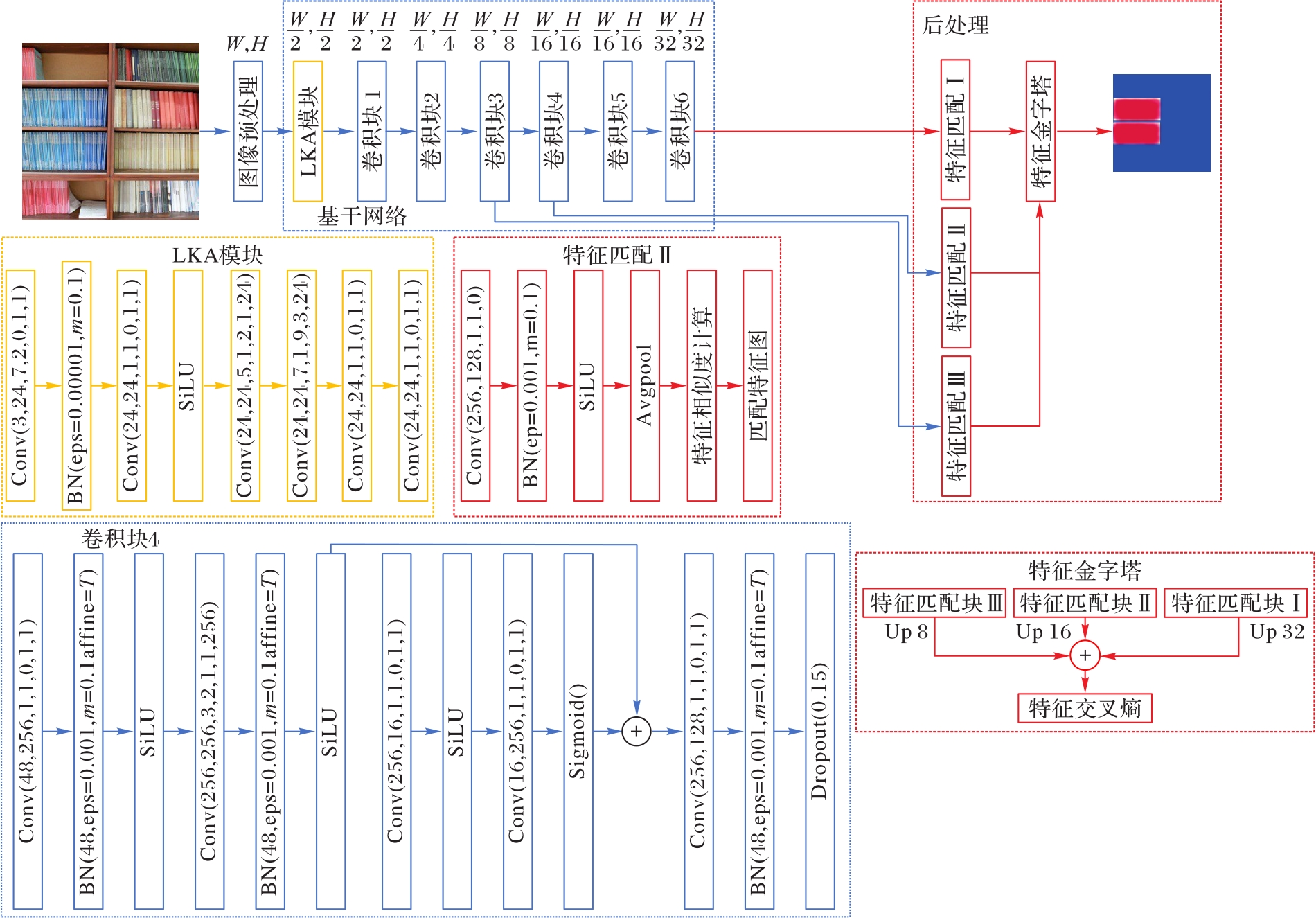
图3 融合大核卷积的轻量级多尺度融合的图像篡改检测算法流程
Fig. 3 Flow chart of image tamper detection algorithm based on lightweight multi-scale fusion with large kernel convolution
| 模块序号 | 模块名称 | 步距 | 输出通道 | 重复层数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Conv3×3 | 2 | 24 | 1 |
| 1 | Fused-MBConv1,K=3×3 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
| 2 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 48 | 4 |
| 3 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 64 | 4 |
| 4 | MBConv4,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 2 | 128 | 6 |
| 5 | MBConv6,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 1 | 160 | 9 |
| 6 | MBConv6,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 2 | 256 | 15 |
表1 原始EfficientNetV2算法的网络结构
Tab. 1 Network structure of original EfficientNetV2 algorithm
| 模块序号 | 模块名称 | 步距 | 输出通道 | 重复层数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Conv3×3 | 2 | 24 | 1 |
| 1 | Fused-MBConv1,K=3×3 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
| 2 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 48 | 4 |
| 3 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 64 | 4 |
| 4 | MBConv4,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 2 | 128 | 6 |
| 5 | MBConv6,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 1 | 160 | 9 |
| 6 | MBConv6,K3×3,SE=0.25 | 2 | 256 | 15 |
| 模块序号 | 模块名称 | 步距 | 输出通道 | 重复层数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | LKA | 2 | 12 | 1 |
| 1 | Fused-MBConv1,K=3×3 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
| 2 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 36 | 4 |
| 3 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 48 | 4 |
| 4 | MBConv4,K,SE=0.25 | 2 | 92 | 6 |
| 5 | MBConv6,K,SE=0.25 | 1 | 128 | 3 |
| 6 | MBConv6,K,SE=0.25 | 2 | 192 | 5 |
表2 LKA-EfficientNet算法的网络结构
Tab. 2 Network structure of LKA-EfficientNet algorithm
| 模块序号 | 模块名称 | 步距 | 输出通道 | 重复层数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | LKA | 2 | 12 | 1 |
| 1 | Fused-MBConv1,K=3×3 | 1 | 24 | 2 |
| 2 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 36 | 4 |
| 3 | Fused-MBConv4,K=3×3 | 2 | 48 | 4 |
| 4 | MBConv4,K,SE=0.25 | 2 | 92 | 6 |
| 5 | MBConv6,K,SE=0.25 | 1 | 128 | 3 |
| 6 | MBConv6,K,SE=0.25 | 2 | 192 | 5 |
| 层数 | 不同基干网络的精度/% | |
|---|---|---|
| EfficinetNetV2 | EfficientNetV2+LKA | |
| 16 | 79.7 | 80.0 |
| 18 | 82.0 | 82.2 |
| 20 | 84.8 | 84.2 |
| 22 | 85.3 | 84.9 |
| 24 | 82.6 | 85.7 |
| 26 | 82.7 | 88.3 |
| 28 | 80.5 | 88.0 |
| 30 | 81.1 | 87.8 |
| 32 | 80.0 | 88.0 |
| 34 | 80.5 | 88.4 |
| 36 | 80.2 | 88.3 |
表3 不同层数的基干网络消融实验结果
Tab. 3 Ablation experimental results of backbone networks with different layers
| 层数 | 不同基干网络的精度/% | |
|---|---|---|
| EfficinetNetV2 | EfficientNetV2+LKA | |
| 16 | 79.7 | 80.0 |
| 18 | 82.0 | 82.2 |
| 20 | 84.8 | 84.2 |
| 22 | 85.3 | 84.9 |
| 24 | 82.6 | 85.7 |
| 26 | 82.7 | 88.3 |
| 28 | 80.5 | 88.0 |
| 30 | 81.1 | 87.8 |
| 32 | 80.0 | 88.0 |
| 34 | 80.5 | 88.4 |
| 36 | 80.2 | 88.3 |
| 网络 | 不同层数的精度/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16层 | 20层 | 24层 | 28层 | |
| ResNet | 81.2 | 82.7 | 84.3 | 83.9 |
| ResNet+LKA | 82.0 | 84.2 | 85.5 | 86.7 |
| ShuffleNet | 79.6 | 81.1 | 81.0 | 79.6 |
| Shufflenet+LKA | 79.8 | 83.2 | 84.7 | 84.8 |
| RegNet | 75.7 | 82.8 | 83.1 | 82.2 |
| RegNet+LKA | 76.0 | 82.5 | 83.5 | 84.5 |
表4 不同层数下各网络的精度对比
Tab. 4 Comparison of accuracy of different networks under different layers
| 网络 | 不同层数的精度/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16层 | 20层 | 24层 | 28层 | |
| ResNet | 81.2 | 82.7 | 84.3 | 83.9 |
| ResNet+LKA | 82.0 | 84.2 | 85.5 | 86.7 |
| ShuffleNet | 79.6 | 81.1 | 81.0 | 79.6 |
| Shufflenet+LKA | 79.8 | 83.2 | 84.7 | 84.8 |
| RegNet | 75.7 | 82.8 | 83.1 | 82.2 |
| RegNet+LKA | 76.0 | 82.5 | 83.5 | 84.5 |
| 层间重复次数 | 精度/% | 层间重复次数 | 精度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2,3,4,5,9 | 88.3 | 1,2,2,3,5,11 | 87.2 |
| 2,4,4,6,3,5 | 90.1 | 1,2,2,4,5,10 | 87.5 |
| 1,3,4,5,4,7 | 89.3 | 2,3,4,5,4,6 | 89.7 |
表5 同一层数时不同层间重复次数的精度对比
Tab. 5 Comparison of accuracy of different repetitions between layers under same number of layers
| 层间重复次数 | 精度/% | 层间重复次数 | 精度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2,3,4,5,9 | 88.3 | 1,2,2,3,5,11 | 87.2 |
| 2,4,4,6,3,5 | 90.1 | 1,2,2,4,5,10 | 87.5 |
| 1,3,4,5,4,7 | 89.3 | 2,3,4,5,4,6 | 89.7 |
| 通道数变化率/% | 精度/% | 通道数变化率/% | 精度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| -30 | 88.7 | 0 | 90.1 |
| -25 | 90.2 | +10 | 87.8 |
| -10 | 89.8 | +25 | 88.0 |
表6 基干网络不同通道数量的精度对比
Tab. 6 Accuracy comparison of different channel numbers in backbone network
| 通道数变化率/% | 精度/% | 通道数变化率/% | 精度/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| -30 | 88.7 | 0 | 90.1 |
| -25 | 90.2 | +10 | 87.8 |
| -10 | 89.8 | +25 | 88.0 |
| 算法 | 浮点运算量/GFLOPs | 参数量/106 | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 14.02 | 33.41 | 0.846 | 0.792 | 0.818 |
| 文献[ | 12.83 | 33.88 | 0.869 | 0.882 | 0.872 |
| 文献[ | 1.32 | 2.80 | 0.855 | 0.868 | 0.861 |
| 文献[ | 5.10 | 20.80 | 0.866 | 0.901 | 0.882 |
| 文献[ | 2.10 | 7.70 | 0.870 | 0.884 | 0.876 |
| 本文算法 | 0.93 | 4.10 | 0.915 | 0.893 | 0.903 |
表7 不同算法的性能对比结果
Tab. 7 Performance comparison results of different algorithms
| 算法 | 浮点运算量/GFLOPs | 参数量/106 | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 14.02 | 33.41 | 0.846 | 0.792 | 0.818 |
| 文献[ | 12.83 | 33.88 | 0.869 | 0.882 | 0.872 |
| 文献[ | 1.32 | 2.80 | 0.855 | 0.868 | 0.861 |
| 文献[ | 5.10 | 20.80 | 0.866 | 0.901 | 0.882 |
| 文献[ | 2.10 | 7.70 | 0.870 | 0.884 | 0.876 |
| 本文算法 | 0.93 | 4.10 | 0.915 | 0.893 | 0.903 |
| 算法 | Dataset | MICC-F2000 | COVERAGE | MICC-F600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 0.482 | 0.642 | 0.574 | 0.703 |
| 文献[ | 0.531 | 0.742 | 0.626 | 0.791 |
| 文献[ | 0.582 | 0.751 | 0.631 | 0.795 |
| 文献[ | 0.580 | 0.754 | 0.615 | 0.788 |
| 文献[ | 0.551 | 0.709 | 0.602 | 0.724 |
| 本文算法 | 0.614 | 0.771 | 0.647 | 0.824 |
表8 不同算法在4个数据集上的F1结果对比
Tab. 8 Comparison of F1 results of different algorithms on four datasets
| 算法 | Dataset | MICC-F2000 | COVERAGE | MICC-F600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文献[ | 0.482 | 0.642 | 0.574 | 0.703 |
| 文献[ | 0.531 | 0.742 | 0.626 | 0.791 |
| 文献[ | 0.582 | 0.751 | 0.631 | 0.795 |
| 文献[ | 0.580 | 0.754 | 0.615 | 0.788 |
| 文献[ | 0.551 | 0.709 | 0.602 | 0.724 |
| 本文算法 | 0.614 | 0.771 | 0.647 | 0.824 |
| 1 | 田秀霞,李华强,张琴,等. 基于双通道R-FCN的图像篡改检测模型[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(2):370-383. 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00370 |
| TIAN X X, LI H Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Dual-channel R-FCN model for image forgery detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(2):370-383. 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.00370 | |
| 2 | GUO M H, LU C Z, LIU Z N, et al. Visual attention network[EB/OL]. (2022-07-11) [2022-07-01].. |
| 3 | ALOM M Z, TAHA T M, YAKOPCIC C, et al. A state-of-the-art survey on deep learning theory and architectures[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8(3): No.292. 10.3390/electronics8030292 |
| 4 | DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A, et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale[EB/OL]. (2021-06-03) [2022-07-01].. |
| 5 | MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M. MobileViT: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[EB/OL]. (2022-03-04) [2022-07-01].. 10.1109/cvpr.2019.00941 |
| 6 | TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNetV2: smaller models and faster training[C]// Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2021: 10096-10106. |
| 7 | FRIDRICH J, SOUKAL D, LUKÁŠ J. Detection of copy-move forgery in digital images[EB/OL]. [2022-06-11].. |
| 8 | COZZOLINO D, POGGI G, VERDOLIVA L. Efficient dense-field copy-move forgery detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(11): 2284-2297. 10.1109/tifs.2015.2455334 |
| 9 | POPESCU A C, FARID H. Exposing digital forgeries by detecting duplicated image regions: TR2004-515[R/OL]. (2004-08-01) [2022-04-11].. 10.1109/tsp.2004.839932 |
| 10 | RUBLEE E, RABAUD V, KONOLIGE K, et al. ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF[C]// Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2011: 2564-2571. 10.1109/iccv.2011.6126544 |
| 11 | TAREEN S A K, SALEEM Z. A comparative analysis of SIFT, SURF, KAZE, AKAZE, ORB, and BRISK[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1-10. 10.1109/icomet.2018.8346440 |
| 12 | RAO Y, NI J Q. A deep learning approach to detection of splicing and copy-move forgeries in images[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Workshop on Information Forensics and Security. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 1-6. 10.1109/wifs.2016.7823911 |
| 13 | WU Y, ABD-ALMAGEED W, NATARAJAN P. BusterNet: detecting copy-move image forgery with source/target localization[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision, LNCS 11210. Cham: Springer, 2018: 170-186. |
| 14 | CHEN B J, TAN W J, COATRIEUX G, et al. A serial image copy-move forgery localization scheme with source/target distinguishment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 3506-3517. 10.1109/tmm.2020.3026868 |
| 15 | ZHOU P, HAN X T, MORARIU V I, et al. Learning rich features for image manipulation detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1053-1061. 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00116 |
| 16 | WU Y, AbdALMAGEED W, NATARAJAN P. ManTra-Net: manipulation tracing network for detection and localization of image forgeries with anomalous features[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 9535-9544. 10.1109/cvpr.2019.00977 |
| 17 | 徐代,岳璋,杨文霞,等. 基于改进的三向流Faster R-CNN的篡改图像识别[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(5):1315-1321. 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019081515 |
| XU D, YUE Z, YANG W X, et al. Tampered image recognition based on improved three-stream Faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40(5):1315-1321. 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2019081515 | |
| 18 | ZHONG J L, PUN C M. An end-to-end Dense-InceptionNet for image copy-move forgery detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15: 2134-2146. 10.1109/tifs.2019.2957693 |
| 19 | 吴旭,刘翔,赵静文. 一种轻量级多尺度融合的图像篡改检测算法[J].计算机工程, 2022, 48(2):224-229, 236. 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0060066 |
| WU X, LIU X, ZHAO J W. A lightweight multiscale fusion algorithm for image tampering detection[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(2):224-229, 236. 10.19678/j.issn.1000-3428.0060066 | |
| 20 | BARNI M, PHAN Q T, TONDI B. Copy move source-target disambiguation through multi-branch CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 1825-1840. 10.1109/tifs.2020.3045903 |
| 21 | LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 936-944. 10.1109/cvpr.2017.106 |
| 22 | SCHROFF F, KALENICHENKO D, PHILBIN J. FaceNet: a unified embedding for face recognition and clustering[C]// Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 815-823. 10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298682 |
| 23 | BEIS J S, LOWE D G. Shape indexing using approximate nearest-neighbour search in high-dimensional spaces[C]// Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 1997: 1000-1006. |
| 24 | DONG J, WANG W, TAN T N. CASIA image tampering detection evaluation database[C]// Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE China Summit and International Conference on Signal and Information Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2013: 422-426. 10.1109/chinasip.2013.6625374 |
| 25 | TRALIC D, ZUPANCIC I, GRGIC S, et al. CoMoFoD — new database for copy-move forgery detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2013 International Symposium on Electronics in Marine. Piscataway: IEEE, 2013: 49-54. |
| 26 | ARDIZZONE E, BRUNO A, MAZZOLA G. Copy-move forgery detection by matching triangles of keypoints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(10): 2084-2094. 10.1109/tifs.2015.2445742 |
| 27 | AMERINI I, BALLAN L, CALDELLI R, et al. A SIFT-based forensic method for copy-move attack detection and transformation recovery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2011, 6(3): 1099-1110. 10.1109/tifs.2011.2129512 |
| 28 | WEN B H, ZHU Y, SUBRAMANIAN R, et al. COVERAGE — a novel database for copy-move forgery detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 161-165. 10.1109/icip.2016.7532339 |
| 29 | AMERINI I, BALLAN L, CALDELLI R, et al. Copy-move forgery detection and localization by means of robust clustering with J-Linkage[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2013, 28(6): 659-669. 10.1016/j.image.2013.03.006 |
| 30 | GOUTTE C, GAUSSIER E. A probabilistic interpretation of precision, recall and F-score, with implication for evaluation[C]// Proceedings of the 2005 European Conference on Information Retrieval, LNCS 3408. Berlin: Springer, 2005: 345-359. |
| 31 | MOLCHANOV P, TYREE S, KARRAS T, et al. Pruning convolutional neural networks for resource efficient inference[EB/OL]. (2017-06-08) [2022-07-01].. |
| 32 | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. 10.1109/cvpr.2016.90 |
| 33 | ZHANG X Y, ZHOU X Y, LIN M X, et al. ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 6848-6856. 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00716 |
| 34 | RADOSAVOVIC I, KOSARAJU R P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Designing network design spaces[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 10425-10433. 10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.01044 |
| 35 | MARRA F, GRAGNANIELLO D, VERDOLIVA L, et al. A full-image full-resolution end-to-end-trainable CNN framework for image forgery detection[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 133488-133502. 10.1109/access.2020.3009877 |
| [1] | 秦璟, 秦志光, 李发礼, 彭悦恒. 基于概率稀疏自注意力神经网络的重性抑郁疾患诊断[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2970-2974. |
| [2] | 李力铤, 华蓓, 贺若舟, 徐况. 基于解耦注意力机制的多变量时序预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2732-2738. |
| [3] | 赵志强, 马培红, 黑新宏. 基于双重注意力机制的人群计数方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2886-2892. |
| [4] | 薛凯鹏, 徐涛, 廖春节. 融合自监督和多层交叉注意力的多模态情感分析网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2387-2392. |
| [5] | 汪雨晴, 朱广丽, 段文杰, 李书羽, 周若彤. 基于交互注意力机制的心理咨询文本情感分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2399. |
| [6] | 高鹏淇, 黄鹤鸣, 樊永红. 融合坐标与多头注意力机制的交互语音情感识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2400-2406. |
| [7] | 李钟华, 白云起, 王雪津, 黄雷雷, 林初俊, 廖诗宇. 基于图像增强的低照度人脸检测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2588-2594. |
| [8] | 莫尚斌, 王文君, 董凌, 高盛祥, 余正涛. 基于多路信息聚合协同解码的单通道语音增强[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2611-2617. |
| [9] | 刘丽, 侯海金, 王安红, 张涛. 基于多尺度注意力的生成式信息隐藏算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2102-2109. |
| [10] | 徐松, 张文博, 王一帆. 基于时空信息的轻量视频显著性目标检测网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2192-2199. |
| [11] | 李大海, 王忠华, 王振东. 结合空间域和频域信息的双分支低光照图像增强网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2175-2182. |
| [12] | 魏文亮, 王阳萍, 岳彪, 王安政, 张哲. 基于光照权重分配和注意力的红外与可见光图像融合深度学习模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2183-2191. |
| [13] | 熊武, 曹从军, 宋雪芳, 邵云龙, 王旭升. 基于多尺度混合域注意力机制的笔迹鉴别方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2225-2232. |
| [14] | 李欢欢, 黄添强, 丁雪梅, 罗海峰, 黄丽清. 基于多尺度时空图卷积网络的交通出行需求预测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2065-2072. |
| [15] | 毛典辉, 李学博, 刘峻岭, 张登辉, 颜文婧. 基于并行异构图和序列注意力机制的中文实体关系抽取模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2018-2025. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||