所属专题: 多媒体计算与计算机仿真
• • 下一篇
许立君1,黎辉2,刘祖阳1,陈侃松1,马为駽1
收稿日期:2023-05-17
修回日期:2023-08-27
接受日期:2023-09-01
发布日期:2026-02-05
出版日期:2024-04-10
通讯作者:
陈侃松
基金资助:
Received:2023-05-17
Revised:2023-08-27
Accepted:2023-09-01
Online:2026-02-05
Published:2024-04-10
Contact:
song kanchen
Supported by:摘要: 脑胶质瘤是由于大脑和脊髓胶质癌变产生的、最常见的原发性颅脑肿瘤,其中恶性脑胶质瘤占比大且死亡率高。利用MRI图像对脑胶质瘤定量分割和分级是目前诊治脑胶质瘤的主要方法。为了提升脑胶质瘤的分割精度与速率,提出了一种基于3D-Ghost卷积神经网络的脑胶质瘤MRI图像分割模型:3D-GA-Unet。该模型以3D-Unet为基础,设计了基于空间注意力机制的3D-ghost卷积神经网络模块,利用线性运算增加有用信息输出、减少传统卷积神经网络中的冗余特征;添加了基于空间的注意力机制模块,有利于获取更多于分割精度有利的图像信息;在公共脑胶质瘤数据集BraTS2018进行训练和验证。实验结果表明3D-GA-Unet脑胶质瘤分割结果的水肿区域、核心区域和增强区域的平均Dice Score分别达到0.86,0.85,0.80,平均敏感度分别达到0.86,0.94,0.83。本文设计网络模块能够对脑胶质瘤图像进行精确分割,进一步提升分割效率,对脑胶质瘤的临床诊断有积极的意义。
中图分类号:
许立君 黎辉 刘祖阳 陈侃松 马为駽. 3D-GA-Unet:基于3D-Ghost卷积神经网络的脑胶质瘤MRI图像分割算法[J]. 计算机应用, DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023050606.
| 区域名 | 包含真实区域 | 掩码值 | 颜色 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 周围水肿区域(ED) | 2 | 绿色 | 边界包含脑胶质瘤的 所有肿瘤结构 |
| ET | 增强肿瘤区域(ET) | 4 | 黄色 | 通过造影剂显示的 肿瘤区域 |
| TC | 非增强肿瘤核(NET) 坏死核心(NCR) | 1 | 红色 | 脑胶质瘤的核心 部分,包含主要的 肿瘤结构 |
| 背景 | 无 | 0 | 黑色 | 图像中脑胶质瘤 区域外的其他区域 |
表1 BraTS2018数据集脑胶质瘤掩码和颜色说明表
Tab. 1 Mask and color description for glioma in BraTS2018 dataset
| 区域名 | 包含真实区域 | 掩码值 | 颜色 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 周围水肿区域(ED) | 2 | 绿色 | 边界包含脑胶质瘤的 所有肿瘤结构 |
| ET | 增强肿瘤区域(ET) | 4 | 黄色 | 通过造影剂显示的 肿瘤区域 |
| TC | 非增强肿瘤核(NET) 坏死核心(NCR) | 1 | 红色 | 脑胶质瘤的核心 部分,包含主要的 肿瘤结构 |
| 背景 | 无 | 0 | 黑色 | 图像中脑胶质瘤 区域外的其他区域 |
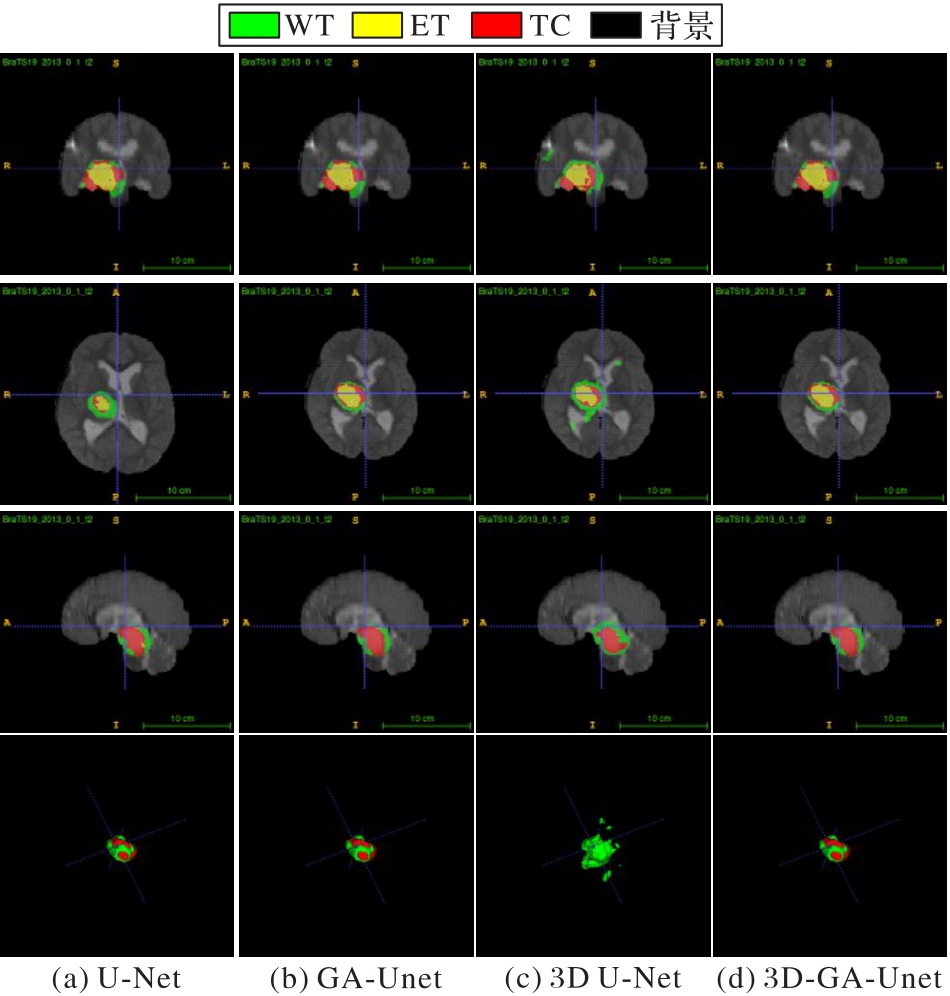
图7 U-Net、GA-Unet、3D U-Net和3D-GA-Unet在BraTS2018上脑胶质瘤的分割结果举例
Fig. 7 Segmentation result examples of U-Net, GA-Unet, 3D U-Net, 3D-GA-Unet for glioma in BraTS2018
| 模型 | DSC | PPV | sensitivity | Hausdorff | 参数量/106 | 收敛 时间/h | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | |||
| U-Net | 0.838 7 | 0.821 5 | 0.768 8 | 0.856 1 | 0.853 3 | 0.774 5 | 0.857 0 | 0.901 4 | 0.829 5 | 2.662 3 | 1.751 1 | 2.846 6 | 16.323 1 | 5.08 |
| GA-Unet | 0.841 3 | 0.836 6 | 0.774 2 | 0.872 8 | 0.863 7 | 0.804 1 | 0.861 3 | 0.905 8 | 0.825 8 | 2.596 9 | 1.717 4 | 2.807 6 | 16.323 4 | 5.30 |
| 3D U-Net | 0.856 2 | 0.851 7 | 0.802 3 | 0.885 1 | 0.867 7 | 0.815 4 | 0.866 9 | 0.914 3 | 0.838 6 | 2.373 9 | 1.615 3 | 2.704 1 | 16.622 9 | 4.94 |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 0.867 3 | 0.826 9 | 0.983 1 | 0.867 6 | 0.949 2 | 0.831 5 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 | 16.333 0 | 4.50 |
表2 在BraTS2018上脑胶质瘤分割结果
Tab. 2 Glioma segmentation results on BraTS2018
| 模型 | DSC | PPV | sensitivity | Hausdorff | 参数量/106 | 收敛 时间/h | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | |||
| U-Net | 0.838 7 | 0.821 5 | 0.768 8 | 0.856 1 | 0.853 3 | 0.774 5 | 0.857 0 | 0.901 4 | 0.829 5 | 2.662 3 | 1.751 1 | 2.846 6 | 16.323 1 | 5.08 |
| GA-Unet | 0.841 3 | 0.836 6 | 0.774 2 | 0.872 8 | 0.863 7 | 0.804 1 | 0.861 3 | 0.905 8 | 0.825 8 | 2.596 9 | 1.717 4 | 2.807 6 | 16.323 4 | 5.30 |
| 3D U-Net | 0.856 2 | 0.851 7 | 0.802 3 | 0.885 1 | 0.867 7 | 0.815 4 | 0.866 9 | 0.914 3 | 0.838 6 | 2.373 9 | 1.615 3 | 2.704 1 | 16.622 9 | 4.94 |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 0.867 3 | 0.826 9 | 0.983 1 | 0.867 6 | 0.949 2 | 0.831 5 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 | 16.333 0 | 4.50 |
| 模型 | DSC | PPV | sensitivity | Hausdorff | 参数量/106 | 收敛 迭代 次数 | 收敛 时间/h | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | ||||
| 3D U-Net | 0.856 2 | 0.851 7 | 0.802 3 | 0.885 1 | 0.867 7 | 0.815 4 | 0.866 9 | 0.914 3 | 0.838 6 | 2.373 9 | 1.615 3 | 2.704 1 | 16.322 9 | 84 | 4.94 |
| 3D U-Net+Ghost | 0.857 3 | 0.840 3 | 0.793 2 | 0.863 4 | 0.868 0 | 0.834 1 | 0.862 0 | 0.915 8 | 0.843 2 | 2.341 2 | 1.605 1 | 2.664 2 | 16.322 7 | 82 | 4.92 |
| 3D U-Net+Attention | 0.858 2 | 0.853 2 | 0.801 6 | 0.875 2 | 0.841 2 | 0.842 4 | 0.861 4 | 0.924 3 | 0.821 3 | 2.213 4 | 1.612 1 | 2.584 1 | 16.334 6 | 79 | 4.81 |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 0.867 3 | 0.826 9 | 0.983 1 | 0.867 6 | 0.949 2 | 0.831 5 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 | 16.333 0 | 69 | 4.50 |
表3 消融实验性能分析
Tab. 3 Performance analysis of ablation experiment
| 模型 | DSC | PPV | sensitivity | Hausdorff | 参数量/106 | 收敛 迭代 次数 | 收敛 时间/h | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | ||||
| 3D U-Net | 0.856 2 | 0.851 7 | 0.802 3 | 0.885 1 | 0.867 7 | 0.815 4 | 0.866 9 | 0.914 3 | 0.838 6 | 2.373 9 | 1.615 3 | 2.704 1 | 16.322 9 | 84 | 4.94 |
| 3D U-Net+Ghost | 0.857 3 | 0.840 3 | 0.793 2 | 0.863 4 | 0.868 0 | 0.834 1 | 0.862 0 | 0.915 8 | 0.843 2 | 2.341 2 | 1.605 1 | 2.664 2 | 16.322 7 | 82 | 4.92 |
| 3D U-Net+Attention | 0.858 2 | 0.853 2 | 0.801 6 | 0.875 2 | 0.841 2 | 0.842 4 | 0.861 4 | 0.924 3 | 0.821 3 | 2.213 4 | 1.612 1 | 2.584 1 | 16.334 6 | 79 | 4.81 |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 0.867 3 | 0.826 9 | 0.983 1 | 0.867 6 | 0.949 2 | 0.831 5 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 | 16.333 0 | 69 | 4.50 |
| 模型 | DSC | Hausdorff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | |
| 文献[ | 0.873 0 | 0.783 0 | 0.754 0 | 5.900 0 | 8.030 0 | 4.530 0 |
| AFPNet[ | 0.865 8 | 0.768 8 | 0.744 3 | — | — | — |
| Task Structure[ | 0.896 0 | 0.824 0 | 0.782 0 | — | — | — |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 |
表4 3D-GA-Unet与先进分割模型对比结果
Tab.4 Comparison results of 3D-GA-Unet and advanced segmentation models
| 模型 | DSC | Hausdorff | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | TC | ET | WT | TC | ET | |
| 文献[ | 0.873 0 | 0.783 0 | 0.754 0 | 5.900 0 | 8.030 0 | 4.530 0 |
| AFPNet[ | 0.865 8 | 0.768 8 | 0.744 3 | — | — | — |
| Task Structure[ | 0.896 0 | 0.824 0 | 0.782 0 | — | — | — |
| 3D-GA-Unet | 0.863 2 | 0.847 3 | 0.803 6 | 2.079 3 | 1.601 2 | 2.573 8 |
| 1 | OSTROM Q T, PATIL N, CIOFFI G, et al. CBTRUS Statistical Report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2013—2017[J]. Neuro-Oncology, 2020, 22(S1): iv1-iv96. 10.1093/neuonc/noaa200 |
| 2 | STUPP R, BRADA M, VAN DEN BENT M J, et al. High-grade malignant glioma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up [J]. Annals of Oncology, 2014, 25(3): 93-101. 10.1093/annonc/mdu050 |
| 3 | LAPOINTE S, PERRY A, BUTOWSKI N A. Primary brain tumours in adults[J].Lancet, 2018, 392(10145): 432-446. 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)30990-5 |
| 4 | WESSELING P, CAPPER D. WHO 2016 classification of gliomas[J]. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 2018, 44(2): 139-150. 10.1111/nan.12432 |
| 5 | 李洁, 刘光耀, 樊凤仙,等. 深度学习和影像组学在脑胶质瘤中的研究进展[J]. 磁共振成像, 2022, 13(4):158-161. 10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2022.04.035 |
| LI J, LIU G Y, FAN F X, et al. Advances in deep learning and imagingomics in glioma[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2022 13(4): 158-161. 10.12015/issn.1674-8034.2022.04.035 | |
| 6 | 姜迪, 刘慧, 李钰,等. 结合稠密特征映射的CT图像肿瘤分割模型[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2021,33(8): 1273-1286. 10.3724/sp.j.1089.2021.18656 |
| JIANG D, LIU H, LI Y, et al. CT image tumor segmentation model combined with dense feature mapping[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2021, 33(8): 1273-1286. 10.3724/sp.j.1089.2021.18656 | |
| 7 | CLAES A, IDEMA A J, WESSELING P. Diffuse glioma growth: a guerilla war[J]. Acta Neuropathologica, 2007, 114(5): 443-458. 10.1007/s00401-007-0293-7 |
| 8 | BELAROUSSI B, MILLES J, CARME S, et al. Intensity non-uniformity correction in MRI: existing methods and their validation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2006, 10(2): 234-246. 10.1016/j.media.2005.09.004 |
| 9 | FRID-ADAR M, DIAMANT I, KLANG E, et al. GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased cnn performance in liver lesion classification [J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 321: 321-331. 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.013 |
| 10 | SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651. 10.1109/tpami.2016.2572683 |
| 11 | NOH H, HONG S, HAN B. Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation [C]// Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015:1520-1528. 10.1109/iccv.2015.178 |
| 12 | CHEN C, LIU X, DING M, et al. 3D dilated multi-fiber network for real-time brain tumor segmentation in MRI[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2019: 184-192. 10.1007/978-3-030-32248-9_21 |
| 13 | CHEN L-C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. 10.1109/tpami.2017.2699184 |
| 14 | BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. 10.1109/tpami.2016.2644615 |
| 15 | DONG H, YANG G, LIU F, et al. Automatic brain tumor detection and segmentation using U-Net based fully convolutional networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 Annual Conference on Medical Image Understanding and Analysis. Cham: Springer, 2017: 506-517. 10.1007/978-3-319-60964-5_44 |
| 16 | 王海鸥,刘慧,郭强,等. 面向医学图像分割的超像素U-Net网络设计[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2019, 31(6):1007-1017. 10.3724/sp.j.1089.2019.17389 |
| WANG H O, LIU H, GUO Q, et al. Design of superpiexl U-Net network for medical image segmentation[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2019,31(6):1007-1017. 10.3724/sp.j.1089.2019.17389 | |
| 17 | ZHOU S, NIE D, ADELI E, et al. High-resolution encoder-decoder networks for low-contrast medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 461-475. 10.1109/tip.2019.2919937 |
| 18 | VALANARASU J M J, SINDAGI V A, HACIHALILOGLU I, et al. KiU-Net: overcomplete convolutional architectures for biomedical image and volumetric segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2022, 41(4): 965-976. 10.1109/tmi.2021.3130469 |
| 19 | QIN X, ZHANG Z, HUANG C, et al. U2-Net: going deeper with nested U-structure for salient object detection [J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 106:107404. 10.1016/j.patcog.2020.107404 |
| 20 | AHMED S F, RAHMAN F S, TABASSUM T, et al. 3D U-Net: fully convolutional neural network for automatic brain tumor segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 22nd International Conference on Computer and Information Technology. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 1-6. 10.1109/iccit48885.2019.9038237 |
| 21 | AboELENIN N M, PIAO S, NOOR A, et al. MIRAU-Net: an improved neural network based on U-Net for gliomas segmentation[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2022, 101: 116553. 10.1016/j.image.2021.116553 |
| 22 | WEN X, ZHAO B, YUAN M, et al. Application of multi-scale fusion attention U-Net to segment the thyroid gland on localized computed tomography images for radiotherapy[J]. Frontiers in Oncology, 2022, 12: 844052. 10.3389/fonc.2022.844052 |
| 23 | YANG S, ZHOU X, WANG J, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptation for cross-device OCT lesion detection via learning adaptive features[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 17th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 1570-1573. 10.1109/isbi45749.2020.9098380 |
| 24 | PEIRIS H, HAYAT M, CHEN Z L, et al. A robust volumetric transformer for accurate 3D tumor segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2022: 162-172. 10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_16 |
| 25 | LI G, ZHANG H, E L, et al. Recognition of honeycomb lung in CT images based on improved MobileNet model[J]. Medical Physics, 2021, 48(8):4304-4315. 10.1002/mp.14873 |
| 26 | ZHANG X, ZHOU X, LIN M, et al. ShuffleNet: an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2018:6848-6856. 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00716 |
| 27 | HAN K, WANG Y, QI T, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2020:1577-1586. 10.1109/cvpr42600.2020.00165 |
| 28 | HOU Q, ZHAN D, FENG J. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2021: 13708-13717. 10.1109/cvpr46437.2021.01350 |
| 29 | MENZE B H, JAKAB A, BAUER S, et al. The multimodal Brain Tumor Image Segmentation Benchmark (BRATS)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2015, 34(10): 1993-2024. 10.1109/tmi.2014.2377694 |
| 30 | WANG G, LI W, OURSELIN S, et al. Automatic brain tumor segmentation based on cascaded convolutional neural networks with uncertainty estimation [J]. Frontiers in Computational Neuroscience, 2019, 13: No.56. 10.3389/fncom.2019.00056 |
| 31 | ZHOU Z, HE Z, JIA Y. AFPNet: a 3D fully convolutional neural network with atrous-convolution feature pyramid for brain tumor segmentation via MRI images [J]. Neurocomputing, 2020,402: 235-244. 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.097 |
| 32 | ZHANG D, HUANG G, ZHANG Q, et al. Exploring task structure for brain tumor segmentation from multi-modality MR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 9032-9043. 10.1109/tip.2020.3023609 |
| [1] | 李玟, 李开荣, 杨凯. 基于数据增强的子图感知对比学习[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 1-9. |
| [2] | 杨兴耀, 齐正, 于炯, 张祖莲, 马帅, 沈洪涛. 时间感知和空间增强的双通道图神经网络会话推荐模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 104-112. |
| [3] | 王丽芳, 任文婧, 郭晓东, 张荣国, 胡立华. 用于低剂量CT图像降噪的多路特征生成对抗网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 270-279. |
| [4] | 马英杰, 覃晶滢, 赵耿, 肖靖. 面向物联网图像的深度压缩感知网络及其混沌加密保护方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 144-151. |
| [5] | 李亚男, 郭梦阳, 邓国军, 陈允峰, 任建吉, 原永亮. 基于多模态融合特征的并分支发动机寿命预测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 305-313. |
| [6] | 何凡, 李理, 苑中旭, 杨秀, 韩东轩. 融合图注意力的概念关联记忆网络知识追踪模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 43-51. |
| [7] | 昝志辉, 王雅静, 李珂, 杨智翔, 杨光宇. 基于SAA-CNN-BiLSTM网络的多特征融合语音情感识别方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2026, 46(1): 69-76. |
| [8] | 卢燕群, 赵奕奕. 基于层次图神经网络和差异化特征学习的客户流失预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 3057-3066. |
| [9] | 张宏俊, 潘高军, 叶昊, 陆玉彬, 缪宜恒. 结合深度学习和张量分解的多源异构数据分析方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2838-2847. |
| [10] | 梁永濠, 李金龙. 用于神经布尔可满足性问题求解器的新型消息传递网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2934-2940. |
| [11] | 邓伊琳, 余发江. 基于LSTM和可分离自注意力机制的伪随机数生成器[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2893-2901. |
| [12] | 刘超, 余岩化. 融合降噪策略与多视图对比学习的知识感知推荐模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2827-2837. |
| [13] | 吕景刚, 彭绍睿, 高硕, 周金. 复频域注意力和多尺度频域增强驱动的语音增强网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2957-2965. |
| [14] | 李维刚, 邵佳乐, 田志强. 基于双注意力机制和多尺度融合的点云分类与分割网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 3003-3010. |
| [15] | 王翔, 陈志祥, 毛国君. 融合局部和全局相关性的多变量时间序列预测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(9): 2806-2816. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||