《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (7): 2301-2310.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021040700
所属专题: 前沿与综合应用
• 前沿与综合应用 • 上一篇
韩泽芳, 张雄( ), 上官宏, 韩兴隆, 韩静, 奉刚, 崔学英
), 上官宏, 韩兴隆, 韩静, 奉刚, 崔学英
收稿日期:2021-05-06
修回日期:2021-10-08
接受日期:2021-10-12
发布日期:2022-07-15
出版日期:2022-07-10
通讯作者:
张雄
作者简介:韩泽芳(1996—),女,山西晋城人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:医学图像处理基金资助:
Zefang HAN, Xiong ZHANG( ), Hong SHANGGUAN, Xinglong HAN, Jing HAN, Gang FENG, Xueying CUI
), Hong SHANGGUAN, Xinglong HAN, Jing HAN, Gang FENG, Xueying CUI
Received:2021-05-06
Revised:2021-10-08
Accepted:2021-10-12
Online:2022-07-15
Published:2022-07-10
Contact:
Xiong ZHANG
About author:HAN Zefang, born in 1996, M. S. candidate. Her research interests include medical image processing.Supported by:摘要:
近年来,生成对抗网络(GAN)用于低剂量CT(LDCT)伪影抑制表现出一定性能优势,已成为该领域新的研究热点。由于伪影分布不规律且与正常组织位置息息相关,现有GAN网络的降噪性能受限。针对上述问题,提出了一种基于伪影感知GAN的LDCT降噪算法。首先,设计了伪影方向感知生成器,该生成器在U型残差编解码结构的基础上增加了伪影方向感知子模块(ADSS),从而提高生成器对伪影方向特征的敏感度;其次,设计了注意力判别器(AttD)来提高对噪声伪影的鉴别能力;最后,设计了与网络功能相对应的损失函数,通过多种损失函数协同作用来提高网络的降噪性能。实验结果表明,与高频敏感GAN(HFSGAN)相比,该降噪算法的平均峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似度(SSIM)分别提升了4.9%和2.8%,伪影抑制效果良好。
中图分类号:
韩泽芳, 张雄, 上官宏, 韩兴隆, 韩静, 奉刚, 崔学英. 用于低剂量CT降噪的伪影感知生成对抗网络[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(7): 2301-2310.
Zefang HAN, Xiong ZHANG, Hong SHANGGUAN, Xinglong HAN, Jing HAN, Gang FENG, Xueying CUI. Artifacts sensing generative adversarial network for low-dose CT denoising[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(7): 2301-2310.

图6 6种降噪算法对受严重横条状伪影污染的胸部LDCT图像的可视化降噪结果
Fig.6 Denoised results of six denoising algorithms for chest LDCT image contaminated by severe horizontal artifacts
| 算法 | PSNR/dB | SSIM | VIF | IFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCT | 26.789 1±1.978 2 | 0.810 0±0.053 5 | 0.364 2±0.057 9 | 2.416 2±0.243 6 |
| BM3D | 30.261 8±1.712 8 | 0.856 6±0.040 8 | 0.385 4±0.047 7 | 2.584 8±0.222 1 |
| RED-CNN | 30.511 4±1.764 7 | 0.866 0±0.041 8 | 0.390 2±0.059 9 | 2.602 2±0.230 5 |
| pix2pix | 28.318 3±1.659 9 | 0.811 1±0.054 5 | 0.334 2±0.054 3 | 2.209 1±0.203 7 |
| HFSGAN | 30.081 8±1.588 9 | 0.852 7±0.044 5 | 0.373 3±0.052 7 | 2.504 5±0.202 7 |
| SiameseGAN | 29.443 9±1.535 0 | 0.861 7±0.042 2 | 0.391 1±0.056 0 | 2.678 6±0.233 0 |
| 本文算法 | 31.543 2±1.720 8 | 0.876 4±0.040 9 | 0.426 2±0.058 3 | 2.934 8±0.249 1 |
表1 不同算法在整个测试集上获取的降噪结果的平均量化指标值统计表(均值±标准差)
Tab.1 Statistical table of average quantization index values of denoised results obtained by different algorithms in whole testing dataset (mean±standard deviation)
| 算法 | PSNR/dB | SSIM | VIF | IFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCT | 26.789 1±1.978 2 | 0.810 0±0.053 5 | 0.364 2±0.057 9 | 2.416 2±0.243 6 |
| BM3D | 30.261 8±1.712 8 | 0.856 6±0.040 8 | 0.385 4±0.047 7 | 2.584 8±0.222 1 |
| RED-CNN | 30.511 4±1.764 7 | 0.866 0±0.041 8 | 0.390 2±0.059 9 | 2.602 2±0.230 5 |
| pix2pix | 28.318 3±1.659 9 | 0.811 1±0.054 5 | 0.334 2±0.054 3 | 2.209 1±0.203 7 |
| HFSGAN | 30.081 8±1.588 9 | 0.852 7±0.044 5 | 0.373 3±0.052 7 | 2.504 5±0.202 7 |
| SiameseGAN | 29.443 9±1.535 0 | 0.861 7±0.042 2 | 0.391 1±0.056 0 | 2.678 6±0.233 0 |
| 本文算法 | 31.543 2±1.720 8 | 0.876 4±0.040 9 | 0.426 2±0.058 3 | 2.934 8±0.249 1 |
| 算法 | SSIM | PSNR/dB | VIF | IFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCT | 0.489 9±0.124 1 | 19.990 5±3.928 5 | 0.163 8±0.040 1 | 1.486 1±0.561 7 |
| BM3D | 0.576 2±0.142 6 | 23.114 4±5.698 5 | 0.232 4±0.063 6 | 1.469 8±0.516 8 |
| RED-CNN | 0.626 8±0.092 0 | 23.805 8±5.118 5 | 0.252 7±0.051 5 | 1.590 3±0.506 0 |
| pix2pix | 0.489 0±0.109 0 | 21.754 8±3.626 2 | 0.152 3±0.046 1 | 1.160 2±0.558 5 |
| HFSGAN | 0.603 4±0.092 4 | 23.786 1±4.189 9 | 0.227 9±0.039 1 | 1.451 2±0.541 2 |
| SiameseGAN | 0.623 6±0.083 8 | 22.832 6±3.507 1 | 0.244 7±0.035 7 | 1.390 5±0.943 1 |
| 本文算法 | 0.651 7±0.079 3 | 24.962 8±4.310 1 | 0.306 4±0.044 4 | 1.729 2±0.468 5 |
表2 图3~6的4个ROI上的平均PSNR和SSIM值(均值±标准差)
Tab.2 Average PSNR and SSIM values on 4 ROIs in Fig. 3 to Fig. 6 (mean±standard deviation)
| 算法 | SSIM | PSNR/dB | VIF | IFC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCT | 0.489 9±0.124 1 | 19.990 5±3.928 5 | 0.163 8±0.040 1 | 1.486 1±0.561 7 |
| BM3D | 0.576 2±0.142 6 | 23.114 4±5.698 5 | 0.232 4±0.063 6 | 1.469 8±0.516 8 |
| RED-CNN | 0.626 8±0.092 0 | 23.805 8±5.118 5 | 0.252 7±0.051 5 | 1.590 3±0.506 0 |
| pix2pix | 0.489 0±0.109 0 | 21.754 8±3.626 2 | 0.152 3±0.046 1 | 1.160 2±0.558 5 |
| HFSGAN | 0.603 4±0.092 4 | 23.786 1±4.189 9 | 0.227 9±0.039 1 | 1.451 2±0.541 2 |
| SiameseGAN | 0.623 6±0.083 8 | 22.832 6±3.507 1 | 0.244 7±0.035 7 | 1.390 5±0.943 1 |
| 本文算法 | 0.651 7±0.079 3 | 24.962 8±4.310 1 | 0.306 4±0.044 4 | 1.729 2±0.468 5 |
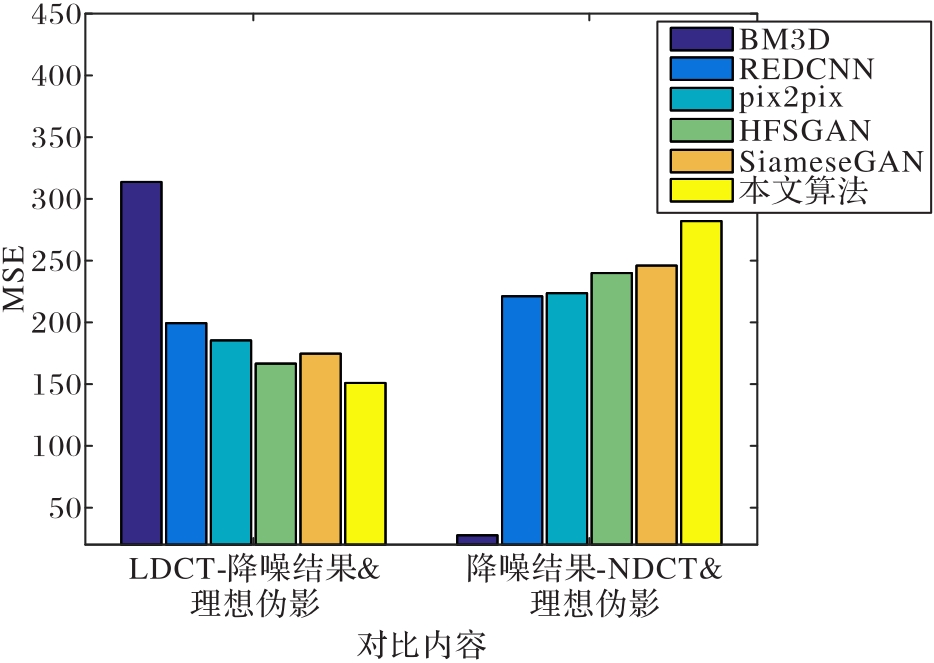
图10 不同算法降噪结果与NDCT(或LDCT)的差值图与理想伪影图的均方误差值
Fig.10 Mean squared error values of difference maps between different denoised results of algorithms and NDCT (or LDCT) and ideal artifact diagrams
| 算法 | 子模块 | 平均SSIM | 平均PSNR/dB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADSS | URED | AttD | |||
| w/o AttD+URED+ADSS | 0.874 7 | 31.378 0 | |||
| w/o AttD+URED | √ | 0.874 6 | 31.390 6 | ||
| w/o AttD | √ | √ | 0.876 5 | 31.521 6 | |
| 本文算法 | √ | √ | √ | 0.876 4 | 31.543 2 |
表3 网络结构消融对算法性能的影响
Tab.3 Influence of network structure ablation on algorithm performance
| 算法 | 子模块 | 平均SSIM | 平均PSNR/dB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADSS | URED | AttD | |||
| w/o AttD+URED+ADSS | 0.874 7 | 31.378 0 | |||
| w/o AttD+URED | √ | 0.874 6 | 31.390 6 | ||
| w/o AttD | √ | √ | 0.876 5 | 31.521 6 | |
| 本文算法 | √ | √ | √ | 0.876 4 | 31.543 2 |
| 算法 | 训练时间/s | 每幅测试时间/s | 参数量 | 迭代 次数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM3D | — | 1.207 8 | — | — |
| RED-CNN | 674.68 | 0.104 1 | 1 848 865 | 30 |
| pix2pix | 4 740.58 | 0.067 9 | 57 190 084 | 30 |
| HFSGAN | 6 522.60 | 0.075 1 | 108 877 962 | 30 |
| SiameseGAN | 55 635.40 | 0.047 5 | 86 829 640 | 30 |
| 本文算法 | 32 177.65 | 0.053 5 | 35 285 594 | 30 |
表4 6种算法的训练与测试时间比较
Tab.4 Comparison of training and testing time of six algorithms
| 算法 | 训练时间/s | 每幅测试时间/s | 参数量 | 迭代 次数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BM3D | — | 1.207 8 | — | — |
| RED-CNN | 674.68 | 0.104 1 | 1 848 865 | 30 |
| pix2pix | 4 740.58 | 0.067 9 | 57 190 084 | 30 |
| HFSGAN | 6 522.60 | 0.075 1 | 108 877 962 | 30 |
| SiameseGAN | 55 635.40 | 0.047 5 | 86 829 640 | 30 |
| 本文算法 | 32 177.65 | 0.053 5 | 35 285 594 | 30 |
| 1 | 张权.低剂量X线CT重建若干问题研究[D]. 南京:东南大学, 2015:1. 10.7666/d.Y2977255 |
| ZHANG Q. A study on some problems in image reconstruction for low-dose CT system[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2015:1. 10.7666/d.Y2977255 | |
| 2 | ALIASGHARZADEH A, MIHANDOOST E, MOHSENI M. A survey of computed tomography dose index and dose length product level in usual computed tomography protocol[J]. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics, 2018, 14(3): 549. 10.4103/0973-1482.172713 |
| 3 | BUADES A, COLL B, MOREL J M. A non-local algorithm for image denoising[C]// Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2005: 60-65. |
| 4 | FERUGLIO P F, VINEGONI C, GROS J, et al. Block matching 3D random noise filtering for absorption optical projection tomography[J]. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2010, 55(18): No.5401. 10.1088/0031-9155/55/18/009 |
| 5 | 代晓婷,龚敬,聂生东. 基于结构联合字典的肺部LDCT图像降噪[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(6):1445-1453. 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.06.025 |
| DAI X T, GONG J, NIE S D. Low-dose lung CT image denoising using joint structural dictionary[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(6):1445-1453. 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.06.025 | |
| 6 | CHEN W B, SHAO Y L, JIA L N, et al. Low-dose CT image denoising model based on sparse representation by stationarily classified sub-dictionaries[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 116859-116874. 10.1109/access.2019.2932754 |
| 7 | LIU W B, WANG Z D, LIU X H, et al. A survey of deep neural network architectures and their applications[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 234: 11-26. 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.038 |
| 8 | CHEN H, ZHANG Y, ZHANG W H, et al. Low-dose CT via convolutional neural network[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2017, 8(2): 679-694. 10.1364/boe.8.000679 |
| 9 | SHAN H M, ZHANG Y, YANG Q S, et al. 3-D convolutional encoder-decoder network for low-dose CT via transfer learning from a 2-D trained network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1522-1534. 10.1109/tmi.2018.2832217 |
| 10 | CHEN H, ZHANG Y, KALRA M K, et al. Low-dose CT with a residual encoder-decoder convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2524-2535. 10.1109/tmi.2017.2715284 |
| 11 | WU D F, KIM K, FAKHRI G EL, et al. A cascaded convolutional neural network for X-ray low-dose CT image denoising[EB/OL]. (2017-08-28) [2021-04-20].. |
| 12 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, LNCS 9351. Cham: Springer, 2015: 234-241. |
| 13 | LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 936-944. 10.1109/cvpr.2017.106 |
| 14 | YANG Q S, YAN P K, KALRA M K, et al. CT image denoising with perceptive deep neural networks[EB/OL]. (2017-02-22) [2021-04-20].. 10.1007/978-3-030-13969-8_14 |
| 15 | LIU H Y, JIANG B, SONG Y B, et al. Rethinking image inpainting via a mutual encoder-decoder with feature equalizations[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 European Conference on Computer Vision, LNCS 12347. Cham: Springer, 2020: 725-741. |
| 16 | GOODFELLOW I J, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]// Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2014: 2672-2680. |
| 17 | WOLTERINK J M, LEINER T, VIERGEVER M A, et al. Generative adversarial networks for noise reduction in low-dose CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(12):2536-2545. 10.1109/tmi.2017.2708987 |
| 18 | YI X, BABYN P. Sharpness-aware low-dose CT denoising using conditional generative adversarial network[J]. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2018, 31(5): 655-669. 10.1007/s10278-018-0056-0 |
| 19 | DENTON E, CHINTALA S, SZLAM A, et al. Deep generative image models using a Laplacian pyramid of adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2015: 1486-1494. |
| 20 | ZHANG H, XU T, LI H S, et al. StackGAN: text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 5908-5916. 10.1109/iccv.2017.629 |
| 21 | LI M, HSU W, XIE X D, et al. SACNN: self-attention convolutional neural network for low-dose CT denoising with self-supervised perceptual loss network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(7):2289-2301. 10.1109/tmi.2020.2968472 |
| 22 | ISOLA P, ZHU J Y, ZHOU T H, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 5967-5976. 10.1109/cvpr.2017.632 |
| 23 | YANG L, SHANGGUAN H, ZHANG X, et al. High-frequency sensitive generative adversarial network for low-dose CT image denoising[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 930-943. 10.1109/access.2019.2961983 |
| 24 | HUANG X S, LI S Z, WANG Y S. Jensen-Shannon boosting learning for object recognition[C]// Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2005: 144-149. |
| 25 | ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L. Wasserstein GAN[EB/OL]. (2017-12-06) [2021-04-20].. |
| 26 | YANG Q S, YAN P K, ZHANG Y B, et al. Low-dose CT image denoising using a generative adversarial network with Wasserstein distance and perceptual loss[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1348-1357. 10.1109/tmi.2018.2827462 |
| 27 | LI X L, YE C, YAN Y J, et al. Low-dose CT image denoising based on improved WGAN-gp[J]. Journal of New Media, 2019, 1(2): 75-85. 10.32604/jnm.2019.06259 |
| 28 | GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M, et al. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates Inc., 2017: 5769-5779. |
| 29 | MAO X D, LI Q, XIE H R, et al. Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 2813-2821. 10.1109/iccv.2017.304 |
| 30 | PARK H S, BAEK J, YOU S K, et al. Unpaired image denoising using a generative adversarial network in X-ray CT[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7:110414-110425. 10.1109/access.2019.2934178 |
| 31 | American Association of Physicists in Medicine. Low dose CT grand challenge[DS/OL]. [2021-04-20].. 10.1118/1.4957556 |
| 32 | THOMAS L, SLOVIS M D. The ALARA (as low as reasonably achievable) concept in pediatric CT intelligent dose reduction[J]. Pediatric Radiology, 2002, 32(4): 219-220. |
| 33 | KANDE N A, DAKHANE R, DUKKIPATI A, et al. SiameseGAN: a generative model for denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(1): 180-192. 10.1109/tmi.2020.3024097 |
| 34 | YAO S S, LIN W S, OOG E P, et al. Contrast signal-to-noise ratio for image quality assessment[C]// Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE, 2005: 1529771. 10.1109/icip.2005.1529771 |
| 35 | WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. 10.1109/tip.2003.819861 |
| 36 | SHEIKH H R, BOVIK A C. Image information and visual quality[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(2): 430-444. 10.1109/tip.2005.859378 |
| 37 | SHEIKH H R, BOVIK A C, DE VECIANA G. An information fidelity criterion for image quality assessment using natural scene statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2005, 14(12): 2117-2128. 10.1109/tip.2005.859389 |
| 38 | KINGMA D P, BA J L. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30) [2021-04-20].. |
| [1] | 赵志强, 马培红, 黑新宏. 基于双重注意力机制的人群计数方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2886-2892. |
| [2] | 秦璟, 秦志光, 李发礼, 彭悦恒. 基于概率稀疏自注意力神经网络的重性抑郁疾患诊断[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2970-2974. |
| [3] | 李力铤, 华蓓, 贺若舟, 徐况. 基于解耦注意力机制的多变量时序预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2732-2738. |
| [4] | 薛凯鹏, 徐涛, 廖春节. 融合自监督和多层交叉注意力的多模态情感分析网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2387-2392. |
| [5] | 汪雨晴, 朱广丽, 段文杰, 李书羽, 周若彤. 基于交互注意力机制的心理咨询文本情感分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2393-2399. |
| [6] | 高鹏淇, 黄鹤鸣, 樊永红. 融合坐标与多头注意力机制的交互语音情感识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2400-2406. |
| [7] | 李钟华, 白云起, 王雪津, 黄雷雷, 林初俊, 廖诗宇. 基于图像增强的低照度人脸检测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2588-2594. |
| [8] | 莫尚斌, 王文君, 董凌, 高盛祥, 余正涛. 基于多路信息聚合协同解码的单通道语音增强[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2611-2617. |
| [9] | 刘丽, 侯海金, 王安红, 张涛. 基于多尺度注意力的生成式信息隐藏算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2102-2109. |
| [10] | 徐松, 张文博, 王一帆. 基于时空信息的轻量视频显著性目标检测网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2192-2199. |
| [11] | 李大海, 王忠华, 王振东. 结合空间域和频域信息的双分支低光照图像增强网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2175-2182. |
| [12] | 魏文亮, 王阳萍, 岳彪, 王安政, 张哲. 基于光照权重分配和注意力的红外与可见光图像融合深度学习模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2183-2191. |
| [13] | 熊武, 曹从军, 宋雪芳, 邵云龙, 王旭升. 基于多尺度混合域注意力机制的笔迹鉴别方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2225-2232. |
| [14] | 李欢欢, 黄添强, 丁雪梅, 罗海峰, 黄丽清. 基于多尺度时空图卷积网络的交通出行需求预测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2065-2072. |
| [15] | 毛典辉, 李学博, 刘峻岭, 张登辉, 颜文婧. 基于并行异构图和序列注意力机制的中文实体关系抽取模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2018-2025. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||