《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 383-391.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024020253
• 人工智能 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-03-12
修回日期:2024-04-09
接受日期:2024-04-11
发布日期:2024-06-04
出版日期:2025-02-10
通讯作者:
黄章进
作者简介:严雪文(1999—),女,江西赣州人,硕士研究生,CCF会员,主要研究方向:计算机视觉、小样本学习;
基金资助:Received:2024-03-12
Revised:2024-04-09
Accepted:2024-04-11
Online:2024-06-04
Published:2025-02-10
Contact:
Zhangjin HUANG
About author:YAN Xuewen, born in 1999, M. S. candidate. Her research interests include computer vision, few-shot learning.
Supported by:摘要:
基于深度学习的图像分类算法通常依赖大量训练数据,然而在实际场景中通常难以获取足够大规模的高质量标注样本。针对小样本场景下分类模型泛化能力不足的问题,提出一种基于对比学习的小样本图像分类方法。首先,在训练中增加全局对比学习作为辅助目标,从而使特征提取网络从实例中获得更丰富的信息;其次,对问询样本分块并用于计算局部对比损失,从而促进模型获得从局部推断整体的能力;最后,利用显著性检测混合查询样本的重要区域,并构造复杂样本,以增强模型泛化能力。在2个公开数据集miniImageNet和tieredImageNet上进行的5-way 1-shot和5-way 5-shot的图像分类任务实验结果表明:相较于小样本学习的基线模型Meta-Baseline,所提方法在miniImageNet上的分类准确率分别提高了5.97和4.25个百分点,在tieredImageNet上的分类准确率分别提高了3.86和2.84个百分点;并且,所提方法在miniImageNet上的分类准确率比DFR(Disentangled Feature Representation)模型分别提高了1.02和0.72个百分点。可见,所提方法有效提高了小样本图像分类的准确率,具有良好的泛化能力。
中图分类号:
严雪文, 黄章进. 基于对比学习的小样本图像分类方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(2): 383-391.
Xuewen YAN, Zhangjin HUANG. Few-shot image classification method based on contrast learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(2): 383-391.
| 方法 | 特征提取网络 | miniImageNet | tieredImageNet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | ||
| MAML[ | ConvNet-4 | 46.47±0.82 | 62.71±0.71 | 51.67±1.81 | 70.30±1.75 |
| ProtoNet[ | ConvNet-4 | 48.70±1.84 | 63.11±0.92 | 53.31±0.89 | 72.79±0.74 |
| RelationNet[ | ConvNet-4 | 49.31±0.85 | 66.60±0.69 | 54.48±0.93 | 71.32±0.78 |
| MetaOptNet[ | ResNet-12 | 60.33±0.61 | 76.61±0.46 | 65.99±0.72 | 81.56±0.53 |
| Meta-Baseline[ | ResNet-12 | 63.17±0.23 | 79.26±0.17 | 68.62±0.27 | 83.29±0.18 |
| CAN[ | ResNet-12 | 63.85±0.48 | 79.44±0.34 | 69.89±0.51 | 84.23±0.37 |
| DeepEMD[ | ResNet-12 | 65.91±0.82 | 82.41±0.56 | 71.16±0.87 | 86.03±0.58 |
| RFS[ | ResNet-12 | 62.02±0.63 | 79.64±0.44 | 69.74±0.72 | 84.41±0.55 |
| InfoPatch[ | ResNet-12 | 67.67±0.45 | 82.44±0.31 | 71.51±0.52 | 85.44±0.35 |
| DMF[ | ResNet-12 | 67.76±0.46 | 82.71±0.31 | 71.89±0.52 | 85.96±0.35 |
| RENet[ | ResNet-12 | 67.60±0.44 | 82.58±0.30 | 71.61±0.51 | 85.28±0.35 |
| DFR[ | ResNet-12 | 68.12±0.81 | 82.79±0.56 | 72.38±0.95 | 86.00±0.61 |
| APP2S[ | ResNet-12 | 66.25±0.20 | 83.42±0.15 | 72.00±0.22 | 86.23±0.15 |
| DAM[ | ResNet-12 | 60.39±0.21 | 73.84±0.16 | 64.09±0.23 | 78.39±0.18 |
| 本文方法 | ResNet-12 | 69.14±0.46 | 83.51±0.30 | 72.48±0.51 | 86.13±0.38 |
表1 miniImageNet和tieredImageNet数据集上的图像分类准确率 (%)
Tab. 1 Image classification accuracies on miniImageNet and tieredImageNet datasets
| 方法 | 特征提取网络 | miniImageNet | tieredImageNet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | ||
| MAML[ | ConvNet-4 | 46.47±0.82 | 62.71±0.71 | 51.67±1.81 | 70.30±1.75 |
| ProtoNet[ | ConvNet-4 | 48.70±1.84 | 63.11±0.92 | 53.31±0.89 | 72.79±0.74 |
| RelationNet[ | ConvNet-4 | 49.31±0.85 | 66.60±0.69 | 54.48±0.93 | 71.32±0.78 |
| MetaOptNet[ | ResNet-12 | 60.33±0.61 | 76.61±0.46 | 65.99±0.72 | 81.56±0.53 |
| Meta-Baseline[ | ResNet-12 | 63.17±0.23 | 79.26±0.17 | 68.62±0.27 | 83.29±0.18 |
| CAN[ | ResNet-12 | 63.85±0.48 | 79.44±0.34 | 69.89±0.51 | 84.23±0.37 |
| DeepEMD[ | ResNet-12 | 65.91±0.82 | 82.41±0.56 | 71.16±0.87 | 86.03±0.58 |
| RFS[ | ResNet-12 | 62.02±0.63 | 79.64±0.44 | 69.74±0.72 | 84.41±0.55 |
| InfoPatch[ | ResNet-12 | 67.67±0.45 | 82.44±0.31 | 71.51±0.52 | 85.44±0.35 |
| DMF[ | ResNet-12 | 67.76±0.46 | 82.71±0.31 | 71.89±0.52 | 85.96±0.35 |
| RENet[ | ResNet-12 | 67.60±0.44 | 82.58±0.30 | 71.61±0.51 | 85.28±0.35 |
| DFR[ | ResNet-12 | 68.12±0.81 | 82.79±0.56 | 72.38±0.95 | 86.00±0.61 |
| APP2S[ | ResNet-12 | 66.25±0.20 | 83.42±0.15 | 72.00±0.22 | 86.23±0.15 |
| DAM[ | ResNet-12 | 60.39±0.21 | 73.84±0.16 | 64.09±0.23 | 78.39±0.18 |
| 本文方法 | ResNet-12 | 69.14±0.46 | 83.51±0.30 | 72.48±0.51 | 86.13±0.38 |
| 模型 | miniImageNet | |
|---|---|---|
| 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | |
| 基线模型 | 65.03 | 81.08 |
| +复杂样本生成 | 66.13 | 81.97 |
| +对比学习 | 67.79 | 82.40 |
| +混合策略 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
表2 在miniImageNet数据集上的消融实验结果 (%)
Tab. 2 Results of ablation experiments on miniImageNet dataset
| 模型 | miniImageNet | |
|---|---|---|
| 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot | |
| 基线模型 | 65.03 | 81.08 |
| +复杂样本生成 | 66.13 | 81.97 |
| +对比学习 | 67.79 | 82.40 |
| +混合策略 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
| 增强方式 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 仅常规增强 | 68.07 | 82.52 |
| 颜色抖动 | 68.22 | 82.85 |
| 随机灰度 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
| 两者组合 | 68.91 | 83.13 |
表3 在miniImageNet数据集上不同数据增强方式的分类准确率 (%)
Tab. 3 Classification accuracy of different data augmentation methods on miniImageNet dataset
| 增强方式 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 仅常规增强 | 68.07 | 82.52 |
| 颜色抖动 | 68.22 | 82.85 |
| 随机灰度 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
| 两者组合 | 68.91 | 83.13 |
| 混合方式 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 无 | 67.79 | 82.40 |
| mixup[ | 67.56 | 82.01 |
| CutMix[ | 67.77 | 82.48 |
| SmoothMix[ | 67.90 | 83.38 |
| FMix[ | 68.03 | 82.77 |
| ResizeMix[ | 68.44 | 83.66 |
| PatchMix[ | 68.67 | 83.60 |
| 本文方法 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
表4 在miniImageNet数据集上不同混合方式的分类准确率 (%)
Tab. 4 Classification accuracies of different mixing methods on miniImageNet dataset
| 混合方式 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 无 | 67.79 | 82.40 |
| mixup[ | 67.56 | 82.01 |
| CutMix[ | 67.77 | 82.48 |
| SmoothMix[ | 67.90 | 83.38 |
| FMix[ | 68.03 | 82.77 |
| ResizeMix[ | 68.44 | 83.66 |
| PatchMix[ | 68.67 | 83.60 |
| 本文方法 | 69.14 | 83.51 |
| 选择方案 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 无混合 | 67.15 | 81.87 |
| 显著到对应 | 68.56 | 82.97 |
| 显著到显著 | 67.70 | 81.98 |
| 显著到非显著 | 68.23 | 82.48 |
| 非显著到显著 | 67.09 | 81.73 |
| 非显著到非显著 | 66.99 | 81.66 |
表5 在miniImageNet数据集上不同区域选择方案的分类准确率 (%)
Tab. 5 Classification accuracies of different regional selection schemes on miniImageNet dataset
| 选择方案 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 无混合 | 67.15 | 81.87 |
| 显著到对应 | 68.56 | 82.97 |
| 显著到显著 | 67.70 | 81.98 |
| 显著到非显著 | 68.23 | 82.48 |
| 非显著到显著 | 67.09 | 81.73 |
| 非显著到非显著 | 66.99 | 81.66 |
| 损失 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 66.13 | 81.97 | |
| 66.86 | 82.37 | |
| 67.28 | 82.06 | |
| 67.79 | 82.40 |
表6 在miniImageNet数据集上不同损失的分类准确率 (%)
Tab. 6 Classification accuracies of different losses on miniImageNet dataset
| 损失 | 5-way 1-shot | 5-way 5-shot |
|---|---|---|
| 66.13 | 81.97 | |
| 66.86 | 82.37 | |
| 67.28 | 82.06 | |
| 67.79 | 82.40 |
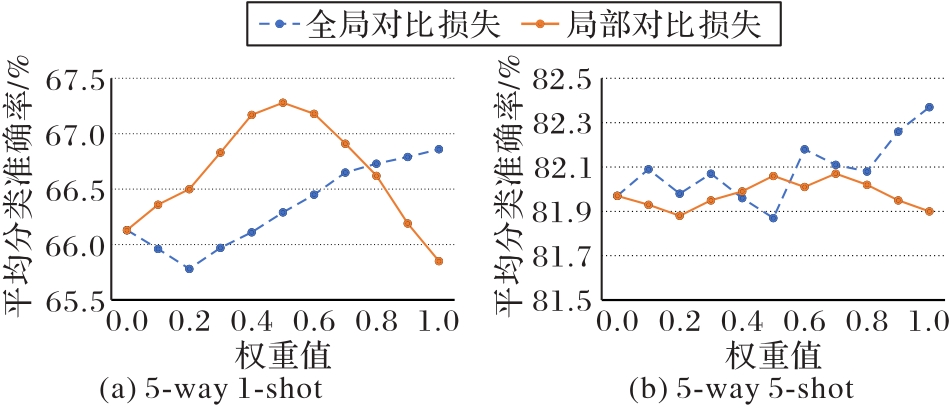
图4 不同超参数时的全局与局部对比损失在miniImageNet数据集上的分类准确率
Fig. 4 Classification accuracies of global and local contrast losses with different hyperparameters on miniImageNet dataset
| 1 | 安胜彪,郭昱岐,白宇,等. 小样本图像分类研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2023, 17(3): 511-532. |
| AN S B, GUO Y Q, BAI Y, et al. Survey of few-shot image classification research[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2023, 17(3): 511-532. | |
| 2 | SIMON C, KONIUSZ P, NOCK R, et al. Adaptive subspaces for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 4135-4144. |
| 3 | XIE J, LONG F, LV J, et al. Joint distribution matters: deep Brownian distance covariance for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 7962-7971. |
| 4 | LI J, WANG Z, HU X. Learning intact features by erasing-inpainting for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021: 8401-8409. |
| 5 | YANG S, LIU L, XU M. Free lunch for few-shot learning: distribution calibration[EB/OL]. [2023-02-06].. |
| 6 | ZHANG B, LI X, FENG S, et al. MetaNODE: prototype optimization as a neural ODE for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2022: 9014-9021. |
| 7 | LI X, SUN Q, LIU Y, et al. Learning to self-train for semi-supervised few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 10276-10286. |
| 8 | 李凡长,刘洋,吴鹏翔,等. 元学习研究综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(2): 422-446. |
| LI F Z, LIU Y, WU P X, et al. A survey on recent advances in meta-learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(2): 422-446. | |
| 9 | TIAN Y, WANG Y, KRISHNAN D, et al. Rethinking few-shot image classification: a good embedding is all you need?[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 European Conference on Computer Vision, LNCS 12359. Cham: Springer, 2020: 266-282. |
| 10 | OUALI Y, HUDELOT C, TAMI M. Spatial contrastive learning for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, LNCS 12975. Cham: Springer, 2021: 671-686. |
| 11 | LIU C, FU Y, XU C, et al. Learning a few-shot embedding model with contrastive learning[C]// Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021: 8635-8643. |
| 12 | 赵凯琳,靳小龙,王元卓. 小样本学习研究综述[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(2): 349-369. |
| ZHAO K L, JIN X L, WANG Y Z. Survey on few-shot learning[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(2): 349-369. | |
| 13 | SNELL J, SWERSKY K, ZEMEL R. Prototypical networks for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2017: 4080-4090. |
| 14 | HOU M, SATO I. A closer look at prototype classifier for few-shot image classification[C]// Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2022: 25767-25778. |
| 15 | TROSTEN D J, CHAKRABORTY R, LØKSE S, et al. Hubs and hyperspheres: reducing hubness and improving transductive few-shot learning with hyperspherical embeddings[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2023: 7527-7536. |
| 16 | JIAN Y, TORRESANI L. Label hallucination for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2022: 7005-7014. |
| 17 | FINN C, ABBEEL P, LEVINE S. Model-agnostic meta-learning for fast adaptation of deep networks[C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2017: 1126-1135. |
| 18 | HU S X, LI D, STÜHMER J, et al. Pushing the limits of simple pipelines for few-shot learning: external data and fine-tuning make a difference[C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 9058-9067. |
| 19 | KHOSLA P, TETERWAK P, WANG C, et al. Supervised contrastive learning[C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2020: 18661-18673. |
| 20 | HE K, FAN H, WU Y, et al. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 9729-9738. |
| 21 | CHEN T, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]// Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2020: 1597-1607. |
| 22 | HÉNAFF O J, SRINIVAS A, DE FAUW J, et al. Data-efficient image recognition with contrastive predictive coding[C]// Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2020: 4182-4192. |
| 23 | DOERSCH C, GUPTA A, ZISSERMAN A. CrossTransformers: spatially-aware few-shot transfer[C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2020: 21981-21993. |
| 24 | YANG Z, WANG J, ZHU Y. Few-shot classification with contrastive learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision, LNCS 13680. Cham: Springer, 2022: 293-309. |
| 25 | HARRIS E, MARCU A, PAINTER M, et al. FMix: enhancing mixed sample data augmentation[EB/OL]. [2024-01-28].. |
| 26 | LEE J H, ZAHEER M Z, ASTRID M, et al. SmoothMix: a simple yet effective data augmentation to train robust classifiers[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 3264-3274. |
| 27 | SHAHAB UDDIN A F M, MONIRA M S, SHIN W, et al. SaliencyMix: a saliency guided data augmentation strategy for better regularization[EB/OL]. [2024-01-30].. |
| 28 | DeVRIES T, TAYLOR G W. Improved regularization of convolutional neural networks with Cutout[EB/OL]. [2024-02-24].. |
| 29 | ZHANG H, CISSE M, DAUPHIN Y N, et al. mixup: beyond empirical risk minimization[EB/OL]. [2024-02-24].. |
| 30 | YUN S, HAN D, CHUN S, et al. CutMix: regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 6022-6031. |
| 31 | LI C, YUAN Y, CAI W, et al. Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking[C]// Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 2710-2717. |
| 32 | ZHOU B, KHOSLA A, LAPEDRIZA A, et al. Learning deep features for discriminative localization[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 2921-2929. |
| 33 | QIN X, ZHANG Z, HUANG C, et al. BASNet: boundary-aware salient object detection[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 7471-7481. |
| 34 | HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 770-778. |
| 35 | MONTABONE S, SOTO A. Human detection using a mobile platform and novel features derived from a visual saliency mechanism[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 2010, 28(3): 391-402. |
| 36 | VINYALS O, BLUNDELL C, LILLICRAP T, et al. Matching networks for one shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2016: 3637-3645. |
| 37 | RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. |
| 38 | CHEN Y, LIU Z, XU H, et al. Meta-Baseline: exploring simple meta-learning for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 9042-9051. |
| 39 | SUNG F, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Learning to compare: relation network for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1199-1208. |
| 40 | LEE K, MAJI S, RAVICHANDRAN A, et al. Meta-learning with differentiable convex optimization[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 10649-10657. |
| 41 | HOU R, CHANG H, MA B, et al. Cross attention network for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 4003-4014. |
| 42 | ZHANG C, CAI Y, LIN G, et al. DeepEMD: few-shot image classification with differentiable earth mover’s distance and structured classifiers[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 12200-12210. |
| 43 | XU C, FU Y, LIU C, et al. Learning dynamic alignment via meta-filter for few-shot learning[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 5178-5187. |
| 44 | KANG D, KWON H, MIN J, et al. Relational embedding for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 8802-8813. |
| 45 | CHENG H, WANG Y, LI H, et al. Disentangled feature representation for few-shot image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(8): 10422-10435. |
| 46 | MA R, FANG P, DRUMMOND T, et al. Adaptive Poincaré point to set distance for few-shot classification[C]// Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2022: 1926-1934. |
| 47 | ZHOU F, ZHANG L, WEI W. Meta-generating deep attentive metric for few-shot classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(10): 6863-6873. |
| 48 | QIN J, FANG J, ZHANG Q, et al. ResizeMix: mixing data with preserved object information and true labels[EB/OL]. [2024-03-07].. |
| 49 | VAN DER MAATEN L, HINTON G. Visualizing data using t-SNE[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 2579-2605. |
| [1] | 杨晟, 李岩. 面向目标检测的对比知识蒸馏方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(2): 354-361. |
| [2] | 郑宗生, 杜嘉, 成雨荷, 赵泽骋, 张月维, 王绪龙. 用于红外-可见光图像分类的跨模态双流交替交互网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(1): 275-283. |
| [3] | 张嘉琳, 任庆桦, 毛启容. 利用全局-局部特征依赖的反欺骗说话人验证系统[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(1): 308-317. |
| [4] | 余肖生, 王智鑫. 基于多层次图对比学习的序列推荐模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(1): 106-114. |
| [5] | 杨兴耀, 陈羽, 于炯, 张祖莲, 陈嘉颖, 王东晓. 结合自我特征和对比学习的推荐模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(9): 2704-2710. |
| [6] | 杨莹, 郝晓燕, 于丹, 马垚, 陈永乐. 面向图神经网络模型提取攻击的图数据生成方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2483-2492. |
| [7] | 徐松, 张文博, 王一帆. 基于时空信息的轻量视频显著性目标检测网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 2192-2199. |
| [8] | 王东炜, 刘柏辰, 韩志, 王艳美, 唐延东. 基于低秩分解和向量量化的深度网络压缩方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(7): 1987-1994. |
| [9] | 翟飞宇, 马汉达. 基于DenseNet的经典-量子混合分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1905-1910. |
| [10] | 蒋小霞, 黄瑞章, 白瑞娜, 任丽娜, 陈艳平. 基于事件表示和对比学习的深度事件聚类方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1734-1742. |
| [11] | 余新言, 曾诚, 王乾, 何鹏, 丁晓玉. 基于知识增强和提示学习的小样本新闻主题分类方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1767-1774. |
| [12] | 汪炅, 唐韬韬, 贾彩燕. 无负采样的正样本增强图对比学习推荐方法PAGCL[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(5): 1485-1492. |
| [13] | 郭洁, 林佳瑜, 梁祖红, 罗孝波, 孙海涛. 基于知识感知和跨层次对比学习的推荐方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(4): 1121-1127. |
| [14] | 肖斌, 杨模, 汪敏, 秦光源, 李欢. 独立性视角下的相频融合领域泛化方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(4): 1002-1009. |
| [15] | 郭安迪, 贾真, 李天瑞. 基于伪实体数据增强的高精准率医学领域实体关系抽取[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(2): 393-402. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
