《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 2604-2610.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2023081197
收稿日期:2023-09-06
修回日期:2023-10-16
接受日期:2023-11-03
发布日期:2024-08-22
出版日期:2024-08-10
通讯作者:
李晨倩
作者简介:李晨倩(1997—),女,河南商丘人,硕士研究生,主要研究方向:机器学习、医学图像处理 2651295321@qq.com
Chenqian LI1,2( ), Jun LIU1,2
), Jun LIU1,2
Received:2023-09-06
Revised:2023-10-16
Accepted:2023-11-03
Online:2024-08-22
Published:2024-08-10
Contact:
Chenqian LI
About author:LIU Jun, born in 1976, Ph. D., professor. His research interests include machine learning, medical image processing.
摘要:
由于超声图像具有噪声强、质量低和边界模糊等特征,获取可靠的注释非常耗时费力,提出基于半监督和多尺度级联注意力的超声颈动脉斑块分割方法。首先,通过不确定性修正金字塔一致性(URPC)的半监督分割方法充分利用未标记数据训练模型减轻费时费力的标注压力。其次,提出一种基于边缘检测的双编码器结构,并利用边缘检测编码器辅助超声斑块图像特征编码器充分获取边缘信息;另外,设计了一个多尺度融合模块(MSFM),通过自适应融合多尺度特征改善提取不规则形状斑块的结果,并结合一个级联通道空间注意力(CCSA)模块更好地关注斑块区域;最后,在超声颈动脉斑块图像数据集上评估所提方法。实验结果表明,所提方法在该数据集上的Dice指标和交并比(IoU)指标比监督方法CA-Net(Comprehensive Attention convolutional neural Network)分别提升了约2.8和6.3个百分点,比半监督方法循环原型一致性学习(CPCL)分别提高了约1.8和1.3个百分点,所提方法可以有效提高超声颈动脉斑块图像的分割准确度。
中图分类号:
李晨倩, 刘俊. 基于半监督和多尺度级联注意力的超声颈动脉斑块分割方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2024, 44(8): 2604-2610.
Chenqian LI, Jun LIU. Ultrasound carotid plaque segmentation method based on semi-supervision and multi-scale cascaded attention[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2024, 44(8): 2604-2610.
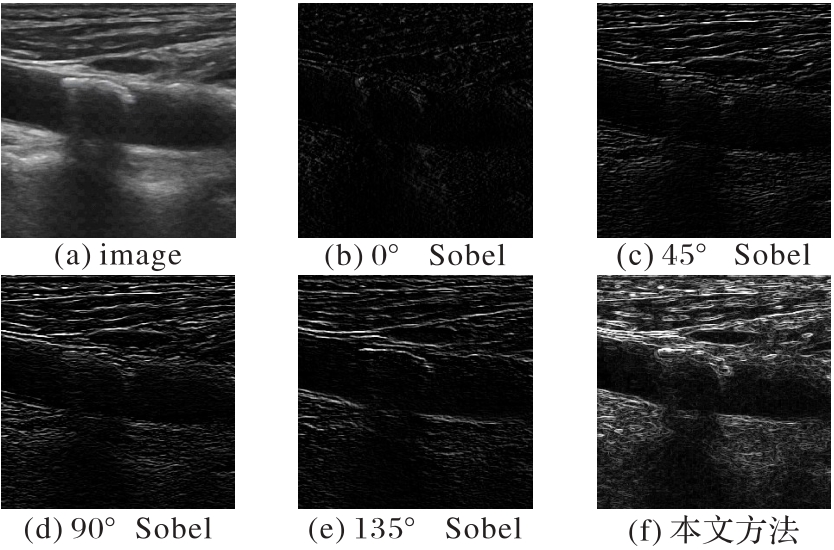
图2 Sobel算子在单个方向上的操作结果和不同方向的组合操作结果
Fig. 2 Results of Sobel operations in a single direction and combination results of Sobel operations in different directions
| 监督方式 | 方法 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全监督 | SegNet[ | 77.61 | 66.93 | 82.20 | 24.76 |
| CA-Net[ | 78.85 | 67.47 | 85.48 | 24.92 | |
| 半监督 | UA-MT[ | 78.43 | 68.03 | 83.86 | 19.54 |
| CPS[ | 79.05 | 72.15 | 87.51 | 20.53 | |
| CPCL[ | 79.83 | 72.40 | 88.01 | 19.08 | |
| 本文方法 | 81.63 | 73.74 | 88.72 | 17.96 |
表1 本文方法和经典方法的实验结果对比
Tab. 1 Experimental result comparison of proposed method and classic methods
| 监督方式 | 方法 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全监督 | SegNet[ | 77.61 | 66.93 | 82.20 | 24.76 |
| CA-Net[ | 78.85 | 67.47 | 85.48 | 24.92 | |
| 半监督 | UA-MT[ | 78.43 | 68.03 | 83.86 | 19.54 |
| CPS[ | 79.05 | 72.15 | 87.51 | 20.53 | |
| CPCL[ | 79.83 | 72.40 | 88.01 | 19.08 | |
| 本文方法 | 81.63 | 73.74 | 88.72 | 17.96 |
| 标注数据占比/% | 未标注数据占比/% | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0 | 58.43 | 49.52 | 68.35 | 37.54 |
| 20 | 40 | 63.37 | 54.85 | 73.63 | 32.69 |
| 20 | 60 | 69.84 | 60.58 | 77.25 | 29.67 |
| 20 | 80 | 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
表2 不同标记数据量的实验结果
Tab. 2 Experimental results with different amounts of labeled data
| 标注数据占比/% | 未标注数据占比/% | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0 | 58.43 | 49.52 | 68.35 | 37.54 |
| 20 | 40 | 63.37 | 54.85 | 73.63 | 32.69 |
| 20 | 60 | 69.84 | 60.58 | 77.25 | 29.67 |
| 20 | 80 | 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
| 损失 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73.23 | 63.32 | 74.05 | 30.33 | |
| 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
表3 损失函数有效性验证
Tab. 3 Validity verification of loss functions
| 损失 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73.23 | 63.32 | 74.05 | 30.33 | |
| 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
| 方法 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Encoder | 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
| Dual Encoder | 77.23 | 67.60 | 80.45 | 24.56 |
| Dual Encoder+MSFM | 78.98 | 69.03 | 83.87 | 22.47 |
| Dual Encoder+MSFM+CCSA | 80.24 | 71.58 | 85.94 | 19.14 |
表4 不同模块的有效性验证
Tab. 4 Effectiveness validation of different modules
| 方法 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Encoder | 75.36 | 64.58 | 77.91 | 26.84 |
| Dual Encoder | 77.23 | 67.60 | 80.45 | 24.56 |
| Dual Encoder+MSFM | 78.98 | 69.03 | 83.87 | 22.47 |
| Dual Encoder+MSFM+CCSA | 80.24 | 71.58 | 85.94 | 19.14 |
| 是否加入不确定性修正 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 否 | 80.42 | 72.38 | 87.23 | 19.05 |
| 是 | 81.63 | 73.74 | 88.72 | 17.96 |
表5 不确定性修正技术的有效性
Tab. 5 Effectiveness of uncertainty rectification technique
| 是否加入不确定性修正 | DSC/% | IoU/% | ACC/% | HD/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 否 | 80.42 | 72.38 | 87.23 | 19.05 |
| 是 | 81.63 | 73.74 | 88.72 | 17.96 |
| 方法 | Param/MB | FLOPs/MB | 方法 | Param/MB | FLOPs/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNet[ | 10.4 | 19.8 | CPS[ | 13.7 | 24.8 |
| CA-Net[ | 32.8 | 67.4 | CPCL[ | 28.8 | 37.7 |
| UA-MT[ | 16.5 | 13.3 | 本文方法 | 22.7 | 32.9 |
表6 各方法时间复杂度分析
Tab. 6 Time complexity analysis of each method
| 方法 | Param/MB | FLOPs/MB | 方法 | Param/MB | FLOPs/MB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SegNet[ | 10.4 | 19.8 | CPS[ | 13.7 | 24.8 |
| CA-Net[ | 32.8 | 67.4 | CPCL[ | 28.8 | 37.7 |
| UA-MT[ | 16.5 | 13.3 | 本文方法 | 22.7 | 32.9 |
| 1 | SPENCE J D. Measurement of carotid plaque burden[J]. JAMA Neurology, 2015, 72(4): 383-384. |
| 2 | JAIN P K, SHARMA N, GIANNOPOULOS A A, et al. Hybrid deep learning segmentation models for atherosclerotic plaque in internal carotid artery B-mode ultrasound[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2021, 136: 104721. |
| 3 | ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 6230-6239. |
| 4 | ZHANG Z, LIU Q, WANG Y. Road extraction by deep residual U-net[J]. IEEE Geoscience Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15(5): 749-753. |
| 5 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Cham: Springer, 2015:234-241. |
| 6 | BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R. SegNet: a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481-2495. |
| 7 | XIE M, LI Y, XUE Y, et al. Two-stage and dual-decoder convolutional U-Net ensembles for reliable vessel and plaque segmentation in carotid ultrasound images[C]// Proceedings of the 19th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 1376-1381. |
| 8 | WANG Y, DENG Z, HU X, et al. Deep attentional features for prostate segmentation in ultrasound[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 11073. Cham: Springer, 2018: 523-530. |
| 9 | ZHOU R, AZARPAZHOOH M R, SPENCE J D, et al. Deep learning-based carotid plaque segmentation from B-mode ultrasound images[J]. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 2021, 47(9): 2723-2733. |
| 10 | YUAN Y, LI C, XU L, et al. Parallel network with channel attention and post-processing for carotid arteries vulnerable plaque segmentation in ultrasound images[EB/OL]. (2022-04-18) [2023-05-10].. |
| 11 | VILA M D M, REMESEIRO B, GRAU M, et al. Semantic segmentation with DenseNets for carotid artery ultrasound plaque segmentation and CIMT estimation[J]. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 2020, 103: No.101784. |
| 12 | LI Y, ZOU L, XIONG L, et al. FRDD-Net: automated carotid plaque ultrasound images segmentation using feature remapping and dense decoding[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(3): No.887. |
| 13 | MI S, BAO Q, WEI Z,et al. MBFF-Net:Multi-branch feature fusion network for carotid plaque segmentation in ultrasound[C]// Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention. Cham:Springer, 2021: 313-322. |
| 14 | LI L, HU Z, HUANG Y, et al. Automatic multi-plaque tracking and segmentation in ultrasonic videos[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 74: No.102201. |
| 15 | GAN H, ZHOU R, OU Y, et al. A multi-task learning framework for carotid plaque segmentation and classification from ultrasound images[EB/OL]. (2023-07-02) [2023-08-10].. |
| 16 | YUAN Y, LI C, ZHANG K, et al. HRU-Net: a transfer learning method for carotid artery plaque segmentation in ultrasound images[J]. Diagnostics, 2022, 12(11): No.2852. |
| 17 | HU X, CAO Y, HU W, et al. Refined feature-based multi-frame and multi-scale fusing gate network for accurate segmentation of plaques in ultrasound videos[J]. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2023, 136: No.107091. |
| 18 | 刘少鹏,洪佳明,梁杰鹏,等. 面向医学图像分割的半监督条件生成对抗网络[J]. 软件学报, 2020, 31(8): 2588-2602. |
| LIU S P, HONG J M, LIANG J P, et al. Medical image segmentation using semi-supervised conditional generative adversarial nets[J]. Journal of Software, 2020, 31(8): 2588-2602. | |
| 19 | 付利华,赵宇,姜涵煦,等. 基于前景感知视觉注意的半监督视频目标分割[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(1): 195-206. |
| FU L H, ZHAO Y, JIANG H X, et al. Semi-supervised video object segmentation based on foreground-aware visual attention[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(1): 195-206. | |
| 20 | YU L, WANG S, LI X, et al. Uncertainty-aware self-ensembling model for semi-supervised 3D left atrium segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, LNCS 11765. Cham: Springer, 2019: 605-613. |
| 21 | LI X, YU L, CHEN H, et al. Semi-supervised skin lesion segmentation via transformation consistent self-ensembling model[EB/OL]. [2023-02-15]. . |
| 22 | FANG K, LI W J. DMNet: difference minimization network for semi-supervised segmentation in medical images[C]// Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, LNCS 12261. Cham: Springer, 2020: 532-541. |
| 23 | HUNG W C, TSAI Y H, LIOU Y T, et al. Adversarial learning for semi-supervised semantic segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 British Machine Vision Conference. Durham: BMVA Press, 2018: 1-12. |
| 24 | JIANG B, CHEN S, WANG B, et al. MGLNN: semi-supervised learning via multiple graph cooperative learning neural networks[J]. Neural Networks, 2022, 153: 204-214. |
| 25 | HUANG W, CHEN C, XIONG Z, et al. Semi-supervised neuron segmentation via reinforced consistency learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2022, 41(11): 3016-3028. |
| 26 | YANG X, HU X, ZHOU S, et al. Interpolation-based contrastive learning for few-label semi-supervised learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(2): 2054-2065. |
| 27 | KITTLER J. On the accuracy of the Sobel edge detector[J]. Image and Vision Computing, 1983, 1(1): 37-42. |
| 28 | WANG X, JIANG X, DING H, et al. Bi-directional dermoscopic feature learning and multi-scale consistent decision fusion for skin lesion segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 3039-3051. |
| 29 | GAO C, YE H, CAO F, et al. Multiscale fused network with additive channel-spatial attention for image segmentation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 214: No.106754. |
| 30 | LUO X, WANG G, LIAO W, et al. Semi-supervised medical image segmentation via uncertainty rectified pyramid consistency[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2022, 80: No.102517. |
| 31 | ZHENG Z, YANG Y. Rectifying pseudo label learning via uncertainty estimation for domain adaptive semantic segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1106-1120. |
| 32 | GRANDVALET Y, BENGIO Y. Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization[C]// Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2004: 529-536. |
| 33 | VU T H, JAIN H, BUCHER M, et al. ADVENT: adversarial entropy minimization for domain adaptation in semantic segmentation[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 2512-2521. |
| 34 | GU R, WANG G, SONG T, et al. CA-Net: comprehensive attention convolutional neural networks for explainable medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2021, 40(2): 699-711. |
| 35 | CHEN X, YUAN Y, ZENG G, et al. Semi-supervised semantic segmentation with cross pseudo supervision[C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 2613-2622. |
| 36 | XU Z, WANG Y, LU D, et al. All-around real label supervision: cyclic prototype consistency learning for semi-supervised medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical Health Informatics, 2022, 26(7): 3174-3184. |
| [1] | 张英俊, 李牛牛, 谢斌红, 张睿, 陆望东. 课程学习指导下的半监督目标检测框架[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2326-2333. |
| [2] | 周妍, 李阳. 用于脑卒中病灶分割的具有注意力机制的校正交叉伪监督方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1942-1948. |
| [3] | 王美, 苏雪松, 刘佳, 殷若南, 黄珊. 时频域多尺度交叉注意力融合的时间序列分类方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1842-1847. |
| [4] | 付顺旺, 陈茜, 李智, 王国美, 卢妤. 用于篡改图像检测和定位的双通道渐进式特征过滤网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(4): 1303-1309. |
| [5] | 张帅华, 张淑芬, 周明川, 徐超, 陈学斌. 基于半监督联邦学习的恶意流量检测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(11): 3487-3494. |
| [6] | 高肇泽, 朱小飞, 项能强. 基于类别感知课程学习的半监督立场检测[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(10): 3281-3287. |
| [7] | 王瑞琪, 纪淑娟, 曹宁, 郭亚杰. 基于一致性训练的半监督虚假招聘广告检测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(9): 2932-2939. |
| [8] | 齐爱玲, 王宣淋. 基于中层细微特征提取与多尺度特征融合细粒度图像识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(8): 2556-2563. |
| [9] | 姜春茂, 吴鹏, 李志聪. 基于Seeds集和成对约束的半监督三支聚类集成[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(5): 1481-1488. |
| [10] | 伏博毅, 彭云聪, 蓝鑫, 秦小林. 基于深度学习的标签噪声学习算法综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(3): 674-684. |
| [11] | 方昕, 黄泽鑫, 张聿晗, 高天, 潘嘉, 付中华, 高建清, 刘俊华, 邹亮. 基于时域波形的半监督端到端虚假语音检测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(1): 227-231. |
| [12] | 李锦烨, 黄瑞章, 秦永彬, 陈艳平, 田小瑜. 基于反绎学习的裁判文书量刑情节识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(6): 1802-1807. |
| [13] | 邱永茹, 姚光乐, 冯杰, 崔昊宇. 基于半监督学习的单幅图像去雨算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(5): 1577-1582. |
| [14] | 殷雨昌, 王洪元, 陈莉, 冯尊登, 肖宇. 基于单标注样本的多损失学习与联合度量视频行人重识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(3): 764-769. |
| [15] | 陆宇, 赵凌云, 白斌雯, 姜震. 基于改进的半监督聚类的不平衡分类算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(12): 3750-3755. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||