《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1422-1429.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022091313
所属专题: 人工智能
收稿日期:2022-09-02
修回日期:2022-11-23
接受日期:2022-11-25
发布日期:2023-02-14
出版日期:2023-05-10
通讯作者:
张凯
作者简介:张凯(1980—),男,湖北武汉人,教授,博士,CCF高级会员,主要研究方向:图神经网络、贝叶斯深度学习、知识追踪、知识图谱 kai.zhang@yangtzeu.edu.cn基金资助:
Kai ZHANG( ), Zhengchu QIN, Yue LIU, Xinyi QIN
), Zhengchu QIN, Yue LIU, Xinyi QIN
Received:2022-09-02
Revised:2022-11-23
Accepted:2022-11-25
Online:2023-02-14
Published:2023-05-10
Contact:
Kai ZHANG
About author:ZHANG Kai, born in 1980, Ph. D., professor. His research interests include graph neural network, Bayesian deep learning, knowledge tracing, knowledge graph.Supported by:摘要:
知识追踪模型主要使用学习过程、学习结束和学习间隔等三类学习行为数据,但现有研究没有融合上述类型的学习行为,无法准确描述多种类型学习行为的相互作用。针对上述问题,提出多学习行为协同的知识追踪(MLB-KT)模型。首先采用多头注意力机制描述每类学习行为的同类约束性,然后采用通道注意力机制建模三类学习行为的多类协同性。将MLB-KT模型与深度知识追踪(DKT)、融合注意力机制的时间卷积知识追踪(ATCKT)模型在3个数据集上进行对比,实验结果表明,MLB-KT模型的曲线下面积(AUC)有明显增加,且在ASSISTments2017数据集上的表现最佳,与DKT、ATCKT模型相比分别提升了12.26%、2.77%;表示质量对比实验的结果也表明MLB-KT模型具有更好的表现。可见建模同类约束性和多类协同性能更好地判断学生的知识状态、预测学生未来的答题情况。
中图分类号:
张凯, 覃正楚, 刘月, 秦心怡. 多学习行为协同的知识追踪模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(5): 1422-1429.
Kai ZHANG, Zhengchu QIN, Yue LIU, Xinyi QIN. Multi-learning behavior collaborated knowledge tracing model[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(5): 1422-1429.
| 数据集 | 学生数 | 学习记录数 | 概念数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assist12 | 46 674 | 5 818 868 | 266 |
| Assist17 | 1 709 | 942 816 | 102 |
| Junyi | 238 120 | 26 666 117 | 684 |
表1 数据集的基本信息
Tab. 1 Basic information of datasets
| 数据集 | 学生数 | 学习记录数 | 概念数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assist12 | 46 674 | 5 818 868 | 266 |
| Assist17 | 1 709 | 942 816 | 102 |
| Junyi | 238 120 | 26 666 117 | 684 |
| 实验配置 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| 操作系统 | Windows 11 |
| CPU | Inter Core i9-9900K CPU@3.60 GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti |
| Python | 3.10 |
| Pytorch | 1.10.2 |
| 内存 | 64 GB |
表2 实验环境
Tab. 2 Experimental environment
| 实验配置 | 参数 |
|---|---|
| 操作系统 | Windows 11 |
| CPU | Inter Core i9-9900K CPU@3.60 GHz |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 Ti |
| Python | 3.10 |
| Pytorch | 1.10.2 |
| 内存 | 64 GB |
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| DKT | 0.717 | 0.726 | 0.814 |
| DKVMN | 0.732 | 0.707 | 0.822 |
| SAKT | 0.691 | 0.734 | 0.853 |
| DKT-F | 0.722 | 0.729 | 0.840 |
| DKT-DT | 0.749 | 0.721 | 0.741 |
| CL4KT | 0.751 | 0.739 | 0.825 |
| ATCKT | 0.762 | 0.793 | 0.847 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
表3 不同模型的AUC对比
Tab. 3 AUC comparison of different models
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| DKT | 0.717 | 0.726 | 0.814 |
| DKVMN | 0.732 | 0.707 | 0.822 |
| SAKT | 0.691 | 0.734 | 0.853 |
| DKT-F | 0.722 | 0.729 | 0.840 |
| DKT-DT | 0.749 | 0.721 | 0.741 |
| CL4KT | 0.751 | 0.739 | 0.825 |
| ATCKT | 0.762 | 0.793 | 0.847 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLB-e | 0.724 | 0.778 | 0.829 |
| MLB-pe | 0.763 | 0.805 | 0.856 |
| MLB-ei | 0.761 | 0.799 | 0.844 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
表4 不同输入数据对模型AUC的影响
Tab. 4 Influence of different input data on AUC of model
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLB-e | 0.724 | 0.778 | 0.829 |
| MLB-pe | 0.763 | 0.805 | 0.856 |
| MLB-ei | 0.761 | 0.799 | 0.844 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLB-B | 0.760 | 0.806 | 0.859 |
| MLB-C | 0.757 | 0.788 | 0.843 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
表5 编码器的消融实验结果
Tab. 5 Ablation experiment result of encoder
| 模型 | Assist12 | Assist17 | Junyi |
|---|---|---|---|
| MLB-B | 0.760 | 0.806 | 0.859 |
| MLB-C | 0.757 | 0.788 | 0.843 |
| MLB-KT | 0.768 | 0.815 | 0.864 |
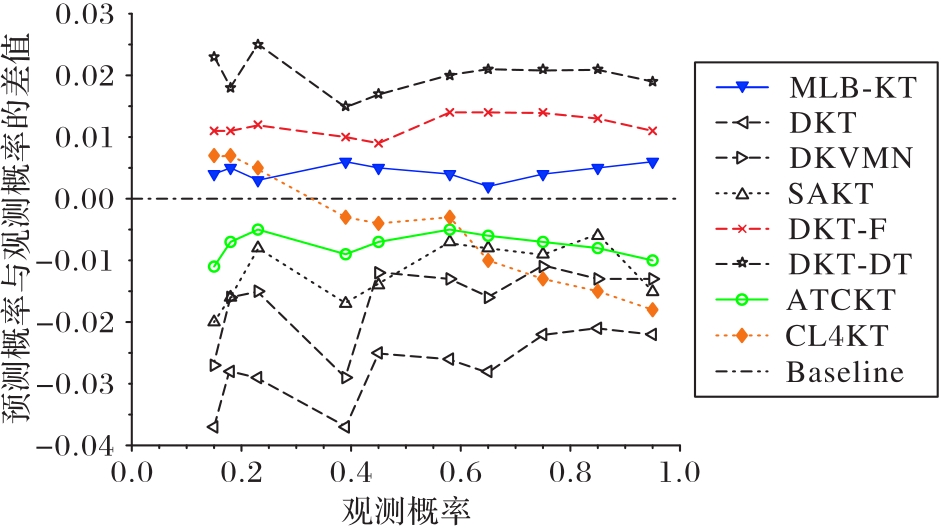
图9 各个模型的校准曲线与差值对齐线的位置关系(以Assist12为例)
Fig. 9 Position relation between calibration curve of each model and difference alignment line (taking Assist12 as an example)
| 1 | LIU Q, SHEN S H, HUANG Z Y, et al. A survey of knowledge tracing[EB/OL]. [2022-02-15].. |
| 2 | CORBETT A T, ANDERSON J R. Knowledge tracing: modeling the acquisition of procedural knowledge[J]. User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction, 1994, 4(4): 253-278. 10.1007/bf01099821 |
| 3 | PIECH C, BASSEN J, HUANG J, et al. Deep knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems — Volume 1. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2015: 505-513. |
| 4 | ZHANG J N, SHI X J, KING I, et al. Dynamic key-value memory networks for knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web. Republic and Canton of Geneva: International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, 2017: 765-774. 10.1145/3038912.3052580 |
| 5 | CHEUNG L P, YANG H Q. Heterogeneous features integration in deep knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Neural Information Processing, LNCS 10635. Cham: Springer, 2017: 653-662. |
| 6 | NAGATANI K, ZHANG Q, SATO M, et al. Augmenting knowledge tracing by considering forgetting behavior[C]// Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference 2019. Republic and Canton of Geneva: International World Wide Web Conferences Steering Committee, 2019: 3101-3107. 10.1145/3308558.3313565 |
| 7 | 李晓光,魏思齐,张昕,等. LFKT: 学习与遗忘融合的深度知识追踪模型[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(3): 818-830. 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006185 |
| LI X G, WEI S Q, ZHANG X, et al. LFKT: deep knowledge tracing model with learning and forgetting behavior merging[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(3): 818-830. 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.006185 | |
| 8 | RABINER L, JUANG B. An introduction to hidden Markov models[J]. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 1986, 3(1): 4-16. 10.1109/massp.1986.1165342 |
| 9 | HINTON G E, SALAKHUTDINOV R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks[J]. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507. 10.1126/science.1127647 |
| 10 | HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 |
| 11 | SANTORO A, BARTUNOV S, BOTVINICK M, et al. Meta-learning with memory-augmented neural networks[C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2016: 1842-1850. |
| 12 | KÄSER T, KLINGLER S, SCHWING A G, et al. Dynamic Bayesian networks for student modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies, 2017, 10(4): 450-462. 10.1109/tlt.2017.2689017 |
| 13 | SU Y, LIU Q W, LIU Q, et al. Exercise-enhanced sequential modeling for student performance prediction[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA: AAAI Press, 2018: 2435-2443. 10.1609/aaai.v32i1.11864 |
| 14 | ABDELRAHMAN G, WANG Q. Knowledge tracing with sequential key-value memory networks[C]// Proceedings of the 42nd International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. New York: ACM, 2019: 175-184. 10.1145/3331184.3331195 |
| 15 | ZHANG K, YAO Y Y. A three learning states Bayesian knowledge tracing model[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 148: 189-201. 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.03.001 |
| 16 | ZHANG K. A three-way c-means algorithm[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 82: No.105536. 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105536 |
| 17 | CHEN P H, LU Y, ZHENG V W, et al. Prerequisite-driven deep knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 39-48. 10.1109/icdm.2018.00019 |
| 18 | LIU S N Y, ZOU R, SUN J W, et al. A hierarchical memory network for knowledge tracing[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 177: No.114935. 10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114935 |
| 19 | EBBINGHAUS H. Memory: a contribution to experimental psychology[J]. Annals of Neurosciences, 2013, 20(4): 155-156. 10.5214/ans.0972.7531.200408 |
| 20 | BAILEY C D. Forgetting and the learning curve: a laboratory study[J]. Management Science, 1989, 35(3): 340-352. 10.1287/mnsc.35.3.340 |
| 21 | 长江大学. 融合学习行为特征的知识追踪方法、系统及存储介质: CN202210746234.5[P]. 2022-09-16. 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109666 |
| Yangtze University. Knowledge tracking method, system and storage medium based on learning behavior features: CN202210746234.5[P]. 2022-09-16. 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109666 | |
| 22 | ZHANG A, LIPTON Z C, LI M, et al. Dive into deep learning[EB/OL]. (2023-02-10) [2023-02-18].. |
| 23 | GHOSH A, HEFFERNAN N, LAN A S. Context-aware attentive knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 26th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. New York: ACM, 2020: 2330-2339. 10.1145/3394486.3403282 |
| 24 | 邵小萌,张猛. 融合注意力机制的时间卷积知识追踪模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(2):343-348. 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022010024 |
| SHAO X M, ZHANG M. Temporal convolutional knowledge tracing model with attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(2):343-348. 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022010024 | |
| 25 | PANDEY S, KARYPIS G. A self-attentive model for knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Educational Data Mining. [S.l.]: International Educational Data Mining Society, 2019: 384-389. |
| 26 | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook, NY: Curran Associates Inc., 2017: 6000-6010. |
| 27 | GUO M H, XU T X, LIU J J, et al. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: a survey[J]. Computational Visual Media, 2022, 8(3): 331-368. 10.1007/s41095-022-0271-y |
| 28 | HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 7132-7141. 10.1109/cvpr.2018.00745 |
| 29 | GAO Z L, XIE J T, WANG Q L, et al. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 3019-3028. 10.1109/cvpr.2019.00314 |
| 30 | LEE H, KIM H E, NAM H. SRM: a style-based recalibration module for convolutional neural networks[C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 1854-1862. 10.1109/iccv.2019.00194 |
| 31 | FITCH W T, HAUSER M D, CHOMSKY N. The evolution of the language faculty: clarifications and implications[J]. Cognition, 2005, 97(2): 179-210. 10.1016/j.cognition.2005.02.005 |
| 32 | National Research Council, Division of Behavioral and Social Sciences and Education, Board on Behavioral, Cognitive, and Sciences Sensory, et al. How People Learn: Brain, Mind, Experience, and School: Expanded Edition[M]. Washington, DC: National Academy Press, 2000: 10-19. 10.17226/6160 |
| 33 | LEE W, CHUN J, LEE Y, et al. Contrastive learning for knowledge tracing[C]// Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2022. New York: ACM, 2022: 2330-2338. 10.1145/3485447.3512105 |
| [1] | 高鹏淇, 黄鹤鸣, 樊永红. 融合坐标与多头注意力机制的交互语音情感识别[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(8): 2400-2406. |
| [2] | 赵雅娟, 孟繁军, 徐行健. 在线教育学习者知识追踪综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(6): 1683-1698. |
| [3] | 李林昊, 张晓倩, 董瑶, 王旭, 董永峰. 基于个性化学习和深层次细化的知识追踪[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(10): 3039-3046. |
| [4] | 姜雨杉, 张仰森. 大语言模型驱动的立场感知事实核查[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2024, 44(10): 3067-3073. |
| [5] | 郑浩东, 马华, 谢颖超, 唐文胜. 融合遗忘因素与记忆门的图神经网络知识追踪模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(9): 2747-2752. |
| [6] | 梁美佳, 刘昕武, 胡晓鹏. 基于改进YOLOv3的列车运行环境图像小目标检测算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(8): 2611-2618. |
| [7] | 蒋瑞林, 覃仁超. 基于深度可分离卷积的多神经网络恶意代码检测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(5): 1527-1533. |
| [8] | 何雪东, 宣士斌, 王款, 陈梦楠. 融合累积分布函数和通道注意力机制的DeepLabV3+图像分割算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(3): 936-942. |
| [9] | 邵小萌, 张猛. 融合注意力机制的时间卷积知识追踪模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(2): 343-348. |
| [10] | 陈炯环, 鲍胜利, 王啸飞, 李若凡. 融合卷积与自注意力机制的基因型填补算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(11): 3534-3539. |
| [11] | 徐丹, 龚红仿, 罗容容. 具有方面项和上下文表示的方面情感分析[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2023, 43(10): 3086-3092. |
| [12] | 屈震, 李堃婷, 冯志玺. 基于有效通道注意力的遥感图像场景分类[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(5): 1431-1439. |
| [13] | 李晓杰, 崔超然, 宋广乐, 苏雅茜, 吴天泽, 张春云. 基于时序超图卷积神经网络的股票趋势预测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2022, 42(3): 797-803. |
| [14] | 高世伟, 张长柱, 王祝萍. 基于可分离金字塔的轻量级实时语义分割算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(10): 2937-2944. |
| [15] | 姚鲁, 宋慧慧, 张开华. 混合阶通道注意力网络的单图像超分辨率重建[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40(10): 3048-3053. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||