《计算机应用》唯一官方网站 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 2113-2122.DOI: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024070932
• CCF第39届中国计算机应用大会 (CCF NCCA 2024) • 上一篇 下一篇
齐巧玲1, 王啸啸2, 张茜茜3( ), 汪鹏2, 董永峰2,4,5
), 汪鹏2, 董永峰2,4,5
收稿日期:2024-07-05
修回日期:2024-10-15
接受日期:2024-10-16
发布日期:2025-07-10
出版日期:2025-07-10
通讯作者:
张茜茜
作者简介:齐巧玲(1984—),女,河北晋州人,讲师,硕士,主要研究方向:人工智能基金资助:
Qiaoling QI1, Xiaoxiao WANG2, Qianqian ZHANG3( ), Peng WANG2, Yongfeng DONG2,4,5
), Peng WANG2, Yongfeng DONG2,4,5
Received:2024-07-05
Revised:2024-10-15
Accepted:2024-10-16
Online:2025-07-10
Published:2025-07-10
Contact:
Qianqian ZHANG
About author:QI Qiaoling, born in 1984, M. S., lecturer. Her research interests include artificial intelligence.Supported by:摘要:
图像分类需要收集大量的图片进行模型训练与优化,但收集过程会不可避免地带来噪声标签。为了应对这一挑战,鲁棒性分类方法应运而生。在目前的鲁棒性分类方法中,超参数的设置需要手动调节,对人力物力带来了大量的损耗。因此,提出元超参数调节器(MHA),采用双层嵌套循环优化的方法自适应地学习噪声感知的超参数组合,并提出Meta-FPL (Feature Pseudo-Label adaptive learning based on Meta learning)算法。此外,为了解决元训练阶段的反向传播过程耗费大量GPU算力的问题,提出选择激活元模型层(SAML)策略。该策略通过比较虚拟训练阶段反向传播的平均梯度与元梯度的大小,限制部分元模型层的更新,从而有效提升模型的训练效率。在4个基准数据集和1个真实数据集上的实验结果表明,与MLC(Meta Label Correction for noisy label learning)、CTRR(ConTrastive RegulaRization)和FPL(Feature Pseudo-Label)算法相比,Meta-FPL算法的分类准确率较高。此外,引入SAML策略后,在元训练阶段的反向传播过程训练时长缩短了79.52%。可见,Meta-FPL算法能在较短的训练时间内有效提升分类测试准确率。
中图分类号:
齐巧玲, 王啸啸, 张茜茜, 汪鹏, 董永峰. 基于元学习的标签噪声自适应学习算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(7): 2113-2122.
Qiaoling QI, Xiaoxiao WANG, Qianqian ZHANG, Peng WANG, Yongfeng DONG. Label noise adaptive learning algorithm based on meta-learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(7): 2113-2122.
| 数据集 | 类别数 | 训练集样本数 | 测试集样本数 | 图片尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | 10 | 60 000 | 10 000 | 28×28 |
| SVHN | 10 | 7 325 | 26 032 | 32×32 |
| CIFAR10 | 10 | 50 000 | 10 000 | 32×32 |
| CIFAR100 | 100 | 50 000 | 10 000 | 32×32 |
| Clothing1M | 14 | 50 000 | 14 000 | 224×224 |
表1 各数据集详细信息
Tab. 1 Details of each datasets
| 数据集 | 类别数 | 训练集样本数 | 测试集样本数 | 图片尺寸 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNIST | 10 | 60 000 | 10 000 | 28×28 |
| SVHN | 10 | 7 325 | 26 032 | 32×32 |
| CIFAR10 | 10 | 50 000 | 10 000 | 32×32 |
| CIFAR100 | 100 | 50 000 | 10 000 | 32×32 |
| Clothing1M | 14 | 50 000 | 14 000 | 224×224 |
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 94.52±0.16 | 78.56±0.36 | 88.93±0.38 | 64.94±0.42 | 91.70±0.20 | 71.26±0.31 | 90.15±0.25 | 69.24±0.41 |
| GCE | 98.99±0.14 | 98.46±0.12 | 99.16±0.11 | 98.75±0.13 | 99.12±0.09 | 99.03±0.14 | 98.28±0.17 | 97.97±0.21 |
| APL | 99.53±0.03 | 99.29±0.03 | 99.22±0.05 | 80.01±0.43 | 99.41±0.04 | 97.22±0.04 | 99.26±0.04 | 87.47±0.44 |
| ELR | 99.22±0.13 | 98.97±0.16 | 99.09±0.10 | 98.99±0.14 | 99.09±0.09 | 99.06±0.15 | 99.05±0.11 | 98.94±0.17 |
| MSLC | 99.07±0.11 | 98.85±0.14 | 99.57±0.10 | 99.33±0.10 | 99.64±0.12 | 99.35±0.14 | 99.58±0.14 | 99.41±0.16 |
| CDR | 94.27±0.35 | 75.76±0.94 | 87.40±0.94 | 62.83±1.57 | 91.40±0.45 | 70.13±1.16 | 89.62±0.53 | 67.40±1.59 |
| PES | 99.57±0.04 | 99.49±0.05 | 99.62±0.02 | 99.58±0.03 | 99.69±0.01 | 99.54±0.03 | 99.51±0.02 | 99.42±0.04 |
| MLC | 98.80±0.04 | 98.47±0.07 | 98.94±0.05 | 97.36±0.06 | 98.91±0.01 | 98.54±0.03 | 98.94±0.03 | 98.42±0.05 |
| CTRR | 98.96±0.24 | 98.16±0.34 | 99.29±0.52 | 99.06±0.47 | 99.01±0.35 | 98.94±0.26 | 98.83±0.28 | 98.14±0.32 |
| FPL | 99.71±0.01 | 99.71±0.02 | 99.72±0.02 | 99.70±0.02 | 99.73±0.02 | 99.70±0.02 | 99.60±0.01 | 99.52±0.02 |
| Meta-FPL | 99.80±0.03 | 99.75±0.05 | 99.83±0.04 | 99.77±0.03 | 99.79±0.04 | 99.72±0.04 | 99.71±0.04 | 99.64±0.05 |
表2 MNIST数据集上后10个训练周期平均测试准确率 ( %)
Tab. 2 Average test accuracy of last 10 epochs on MNIST dataset
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 94.52±0.16 | 78.56±0.36 | 88.93±0.38 | 64.94±0.42 | 91.70±0.20 | 71.26±0.31 | 90.15±0.25 | 69.24±0.41 |
| GCE | 98.99±0.14 | 98.46±0.12 | 99.16±0.11 | 98.75±0.13 | 99.12±0.09 | 99.03±0.14 | 98.28±0.17 | 97.97±0.21 |
| APL | 99.53±0.03 | 99.29±0.03 | 99.22±0.05 | 80.01±0.43 | 99.41±0.04 | 97.22±0.04 | 99.26±0.04 | 87.47±0.44 |
| ELR | 99.22±0.13 | 98.97±0.16 | 99.09±0.10 | 98.99±0.14 | 99.09±0.09 | 99.06±0.15 | 99.05±0.11 | 98.94±0.17 |
| MSLC | 99.07±0.11 | 98.85±0.14 | 99.57±0.10 | 99.33±0.10 | 99.64±0.12 | 99.35±0.14 | 99.58±0.14 | 99.41±0.16 |
| CDR | 94.27±0.35 | 75.76±0.94 | 87.40±0.94 | 62.83±1.57 | 91.40±0.45 | 70.13±1.16 | 89.62±0.53 | 67.40±1.59 |
| PES | 99.57±0.04 | 99.49±0.05 | 99.62±0.02 | 99.58±0.03 | 99.69±0.01 | 99.54±0.03 | 99.51±0.02 | 99.42±0.04 |
| MLC | 98.80±0.04 | 98.47±0.07 | 98.94±0.05 | 97.36±0.06 | 98.91±0.01 | 98.54±0.03 | 98.94±0.03 | 98.42±0.05 |
| CTRR | 98.96±0.24 | 98.16±0.34 | 99.29±0.52 | 99.06±0.47 | 99.01±0.35 | 98.94±0.26 | 98.83±0.28 | 98.14±0.32 |
| FPL | 99.71±0.01 | 99.71±0.02 | 99.72±0.02 | 99.70±0.02 | 99.73±0.02 | 99.70±0.02 | 99.60±0.01 | 99.52±0.02 |
| Meta-FPL | 99.80±0.03 | 99.75±0.05 | 99.83±0.04 | 99.77±0.03 | 99.79±0.04 | 99.72±0.04 | 99.71±0.04 | 99.64±0.05 |
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 87.44±0.34 | 67.09±0.56 | 83.42±0.43 | 60.86±0.37 | 86.0±0.24 | 67.21±0.44 | 83.2±0.45 | 59.55±0.64 |
| GCE | 76.57±0.28 | 60.82±0.30 | 77.83±0.24 | 62.59±0.35 | 78.06±0.19 | 62.98±0.27 | 75.87±0.26 | 60.12±0.34 |
| APL | 77.46±0.31 | 61.05±0.46 | 75.62±0.45 | 59.96±0.47 | 76.06±0.34 | 60.53±0.41 | 75.27±0.44 | 59.83±0.45 |
| ELR | 74.39±0.28 | 56.19±0.23 | 76.94±0.22 | 57.43±0.26 | 75.94±0.28 | 57.16±0.21 | 75.69±0.32 | 58.16±0.27 |
| MSLC | 97.08±0.17 | 95.12±0.14 | 96.97±0.21 | 95.24±0.23 | 97.10±0.18 | 96.88±0.20 | 97.09±0.23 | 96.95±0.25 |
| CDR | 82.46±0.21 | 67.50±2.09 | 82.35±1.39 | 60.41±2.15 | 84.79±1.00 | 64.59±1.44 | 81.96±2.30 | 60.71±3.33 |
| PES | 87.63±0.23 | 69.31±0.37 | 88.92±0.25 | 70.26±0.31 | 89.17±0.19 | 70.34±0.27 | 85.49±0.21 | 67.38±0.36 |
| MLC | 96.75±0.06 | 95.96±0.12 | 96.99±0.11 | 96.06±0.10 | 96.43±0.09 | 95.81±0.11 | 96.38±0.12 | 95.24±0.15 |
| CTRR | 96.21±0.14 | 95.57±0.53 | 97.02±0.21 | 96.20±0.34 | 96.53±0.44 | 96.06±0.45 | 96.17±0.14 | 95.89±0.11 |
| FPL | 97.14±0.02 | 96.87±0.02 | 97.15±0.01 | 97.11±0.02 | 97.14±0.01 | 97.01±0.01 | 97.11±0.01 | 97.02±0.01 |
| Meta-FPL | 97.23±0.04 | 96.98±0.05 | 97.21±0.03 | 97.14±0.04 | 97.26±0.05 | 97.20±0.07 | 97.16±0.06 | 97.09±0.06 |
表3 SVHN数据集上后10个训练周期平均测试准确率 (%)
Tab. 3 Average test accuracy of last 10 epochs on SVHN dataset
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 87.44±0.34 | 67.09±0.56 | 83.42±0.43 | 60.86±0.37 | 86.0±0.24 | 67.21±0.44 | 83.2±0.45 | 59.55±0.64 |
| GCE | 76.57±0.28 | 60.82±0.30 | 77.83±0.24 | 62.59±0.35 | 78.06±0.19 | 62.98±0.27 | 75.87±0.26 | 60.12±0.34 |
| APL | 77.46±0.31 | 61.05±0.46 | 75.62±0.45 | 59.96±0.47 | 76.06±0.34 | 60.53±0.41 | 75.27±0.44 | 59.83±0.45 |
| ELR | 74.39±0.28 | 56.19±0.23 | 76.94±0.22 | 57.43±0.26 | 75.94±0.28 | 57.16±0.21 | 75.69±0.32 | 58.16±0.27 |
| MSLC | 97.08±0.17 | 95.12±0.14 | 96.97±0.21 | 95.24±0.23 | 97.10±0.18 | 96.88±0.20 | 97.09±0.23 | 96.95±0.25 |
| CDR | 82.46±0.21 | 67.50±2.09 | 82.35±1.39 | 60.41±2.15 | 84.79±1.00 | 64.59±1.44 | 81.96±2.30 | 60.71±3.33 |
| PES | 87.63±0.23 | 69.31±0.37 | 88.92±0.25 | 70.26±0.31 | 89.17±0.19 | 70.34±0.27 | 85.49±0.21 | 67.38±0.36 |
| MLC | 96.75±0.06 | 95.96±0.12 | 96.99±0.11 | 96.06±0.10 | 96.43±0.09 | 95.81±0.11 | 96.38±0.12 | 95.24±0.15 |
| CTRR | 96.21±0.14 | 95.57±0.53 | 97.02±0.21 | 96.20±0.34 | 96.53±0.44 | 96.06±0.45 | 96.17±0.14 | 95.89±0.11 |
| FPL | 97.14±0.02 | 96.87±0.02 | 97.15±0.01 | 97.11±0.02 | 97.14±0.01 | 97.01±0.01 | 97.11±0.01 | 97.02±0.01 |
| Meta-FPL | 97.23±0.04 | 96.98±0.05 | 97.21±0.03 | 97.14±0.04 | 97.26±0.05 | 97.20±0.07 | 97.16±0.06 | 97.09±0.06 |
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 83.81±0.15 | 66.22±0.43 | 81.83±0.32 | 59.41±0.60 | 82.97±0.23 | 64.18±0.41 | 81.65±0.42 | 59.02±0.42 |
| GCE | 89.70±0.23 | 87.62±0.35 | 89.83±0.19 | 87.61±0.48 | 90.35±0.04 | 86.63±0.06 | 89.45±0.29 | 57.41±0.34 |
| APL | 88.15±0.09 | 81.51±0.17 | 86.07±0.09 | 51.66±0.20 | 77.34±0.23 | 32.66±0.26 | 78.83±2.11 | 60.00±1.71 |
| ELR | 89.42±0.11 | 87.52±0.10 | 89.87±0.10 | 89.36±0.16 | 88.96±0.09 | 88.48±0.14 | 89.78±0.13 | 90.05±0.17 |
| MSLC | 93.20±0.09 | 90.67±0.17 | 94.09±0.09 | 92.74±0.11 | 92.82±0.11 | 92.44±0.11 | 92.46±0.10 | 91.93±0.14 |
| CDR | 82.79±0.66 | 64.16±0.74 | 81.25±0.96 | 60.17±0.94 | 82.14±0.60 | 64.13±1.13 | 81.11±0.80 | 62.69±1.51 |
| PES | 92.48±0.06 | 89.17±0.13 | 92.14±0.03 | 88.77±0.09 | 92.40±0.05 | 88.70±0.08 | 91.57±0.07 | 89.27±0.12 |
| MLC | 89.46±0.12 | 86.53±0.24 | 90.33±0.15 | 90.30±0.14 | 90.31±0.15 | 90.29±0.13 | 89.74±0.13 | 89.51±0.14 |
| CTRR | 92.97±0.32 | 92.16±0.31 | 93.05±0.56 | 92.82±0.27 | 93.89±0.39 | 93.04±0.33 | 91.67±0.25 | 90.16±0.50 |
| FPL | 93.55±0.03 | 92.92±0.04 | 94.13±0.07 | 94.08±0.09 | 94.23±0.06 | 93.71±0.06 | 93.70±0.06 | 93.50±0.04 |
| Meta-FPL | 93.60±0.05 | 93.01±0.05 | 94.20±0.06 | 94.12±0.07 | 94.32±0.07 | 93.78±0.06 | 93.77±0.05 | 93.60±0.08 |
表4 CIFAR10数据集上后10个训练周期平均测试准确率 (%)
Tab. 4 Average test accuracy of last 10 epochs on CIFAR10 dataset
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 83.81±0.15 | 66.22±0.43 | 81.83±0.32 | 59.41±0.60 | 82.97±0.23 | 64.18±0.41 | 81.65±0.42 | 59.02±0.42 |
| GCE | 89.70±0.23 | 87.62±0.35 | 89.83±0.19 | 87.61±0.48 | 90.35±0.04 | 86.63±0.06 | 89.45±0.29 | 57.41±0.34 |
| APL | 88.15±0.09 | 81.51±0.17 | 86.07±0.09 | 51.66±0.20 | 77.34±0.23 | 32.66±0.26 | 78.83±2.11 | 60.00±1.71 |
| ELR | 89.42±0.11 | 87.52±0.10 | 89.87±0.10 | 89.36±0.16 | 88.96±0.09 | 88.48±0.14 | 89.78±0.13 | 90.05±0.17 |
| MSLC | 93.20±0.09 | 90.67±0.17 | 94.09±0.09 | 92.74±0.11 | 92.82±0.11 | 92.44±0.11 | 92.46±0.10 | 91.93±0.14 |
| CDR | 82.79±0.66 | 64.16±0.74 | 81.25±0.96 | 60.17±0.94 | 82.14±0.60 | 64.13±1.13 | 81.11±0.80 | 62.69±1.51 |
| PES | 92.48±0.06 | 89.17±0.13 | 92.14±0.03 | 88.77±0.09 | 92.40±0.05 | 88.70±0.08 | 91.57±0.07 | 89.27±0.12 |
| MLC | 89.46±0.12 | 86.53±0.24 | 90.33±0.15 | 90.30±0.14 | 90.31±0.15 | 90.29±0.13 | 89.74±0.13 | 89.51±0.14 |
| CTRR | 92.97±0.32 | 92.16±0.31 | 93.05±0.56 | 92.82±0.27 | 93.89±0.39 | 93.04±0.33 | 91.67±0.25 | 90.16±0.50 |
| FPL | 93.55±0.03 | 92.92±0.04 | 94.13±0.07 | 94.08±0.09 | 94.23±0.06 | 93.71±0.06 | 93.70±0.06 | 93.50±0.04 |
| Meta-FPL | 93.60±0.05 | 93.01±0.05 | 94.20±0.06 | 94.12±0.07 | 94.32±0.07 | 93.78±0.06 | 93.77±0.05 | 93.60±0.08 |
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 56.78±0.20 | 38.09±0.25 | 58.27±0.11 | 41.52±0.17 | 59.99±0.13 | 44.25±0.33 | 55.10±0.37 | 36.78±0.26 |
| GCE | 65.24±0.56 | 62.39± 0.38 | 66.21±0.09 | 57.62±0.12 | 64.79±0.11 | 58.35±0.13 | 61.87±0.39 | 47.66±0.69 |
| APL | 56.41±0.11 | 46.25±0.11 | 56.00±0.14 | 41.95±0.16 | 56.40±0.14 | 45.08±0.11 | 55.46±0.12 | 44.68±0.16 |
| ELR | 70.83±0.19 | 66.91±0.21 | 73.46±0.13 | 71.69±0.17 | 72.60±0.16 | 72.48±0.20 | 70.09±0.13 | 69.59±0.19 |
| MSLC | 71.47±0.20 | 67.50±0.14 | 72.62±0.13 | 71.79±0.24 | 72.33±0.08 | 71.71±0.12 | 70.82±0.11 | 69.04±0.15 |
| CDR | 58.45±0.27 | 52.56±0.34 | 63.62±0.26 | 45.82±0.25 | 65.39±0.31 | 48.89±0.35 | 61.70±0.56 | 43.00±0.85 |
| PES | 69.26±0.07 | 64.96±0.14 | 70.67±0.05 | 64.85±0.12 | 71.43±0.13 | 67.40±0.18 | 68.30±0.07 | 66.27±0.16 |
| MLC | 50.92±0.22 | 39.76±0.13 | 58.85±0.23 | 48.88±0.14 | 58.85±0.23 | 48.87±0.14 | 50.67±0.17 | 47.72±0.22 |
| CTRR | 70.09±0.45 | 65.32±0.20 | 72.88±0.34 | 66.75±0.28 | 73.12±0.42 | 64.46±0.17 | 70.15±0.23 | 64.53±0.17 |
| FPL | 71.55±0.08 | 67.84±0.04 | 73.43±0.09 | 72.35±0.09 | 73.26±0.03 | 72.62±0.07 | 71.49±0.05 | 70.34±0.05 |
| Meta-FPL | 71.58±0.06 | 67.86±0.07 | 73.47±0.07 | 72.41±0.09 | 73.24±0.05 | 72.68±0.08 | 71.44±0.06 | 70.38±0.05 |
表5 CIFAR100数据集上后10个训练周期平均测试准确率 (%)
Tab. 5 Average test accuracy of last 10 epochs of CIFAR100 dataset
| 算法 | Symmetric | Pairflip | Tridiagonal | Instance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | NR为20% | NR为40% | |
| Standard | 56.78±0.20 | 38.09±0.25 | 58.27±0.11 | 41.52±0.17 | 59.99±0.13 | 44.25±0.33 | 55.10±0.37 | 36.78±0.26 |
| GCE | 65.24±0.56 | 62.39± 0.38 | 66.21±0.09 | 57.62±0.12 | 64.79±0.11 | 58.35±0.13 | 61.87±0.39 | 47.66±0.69 |
| APL | 56.41±0.11 | 46.25±0.11 | 56.00±0.14 | 41.95±0.16 | 56.40±0.14 | 45.08±0.11 | 55.46±0.12 | 44.68±0.16 |
| ELR | 70.83±0.19 | 66.91±0.21 | 73.46±0.13 | 71.69±0.17 | 72.60±0.16 | 72.48±0.20 | 70.09±0.13 | 69.59±0.19 |
| MSLC | 71.47±0.20 | 67.50±0.14 | 72.62±0.13 | 71.79±0.24 | 72.33±0.08 | 71.71±0.12 | 70.82±0.11 | 69.04±0.15 |
| CDR | 58.45±0.27 | 52.56±0.34 | 63.62±0.26 | 45.82±0.25 | 65.39±0.31 | 48.89±0.35 | 61.70±0.56 | 43.00±0.85 |
| PES | 69.26±0.07 | 64.96±0.14 | 70.67±0.05 | 64.85±0.12 | 71.43±0.13 | 67.40±0.18 | 68.30±0.07 | 66.27±0.16 |
| MLC | 50.92±0.22 | 39.76±0.13 | 58.85±0.23 | 48.88±0.14 | 58.85±0.23 | 48.87±0.14 | 50.67±0.17 | 47.72±0.22 |
| CTRR | 70.09±0.45 | 65.32±0.20 | 72.88±0.34 | 66.75±0.28 | 73.12±0.42 | 64.46±0.17 | 70.15±0.23 | 64.53±0.17 |
| FPL | 71.55±0.08 | 67.84±0.04 | 73.43±0.09 | 72.35±0.09 | 73.26±0.03 | 72.62±0.07 | 71.49±0.05 | 70.34±0.05 |
| Meta-FPL | 71.58±0.06 | 67.86±0.07 | 73.47±0.07 | 72.41±0.09 | 73.24±0.05 | 72.68±0.08 | 71.44±0.06 | 70.38±0.05 |
| 算法 | 最终 | 最佳 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 67.22 | 64.68 |
| APL | 56.01 | 55.84 |
| ELR | 73.27 | 74.53 |
| MSLC | 73.34 | 73.95 |
| CDR | 63.72 | 63.22 |
| PES | 72.37 | 73.64 |
| MLC | 73.28 | 75.61 |
| CTRR | 72.71 | 73.68 |
| FPL | 73.54 | 73.57 |
| Meta-FPL | 73.61 | 73.94 |
表6 Clothing1M数据集上最终和最佳的测试准确率 (%)
Tab. 6 Accuracy of best and last test accuracies on Clothing1M dataset
| 算法 | 最终 | 最佳 |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 67.22 | 64.68 |
| APL | 56.01 | 55.84 |
| ELR | 73.27 | 74.53 |
| MSLC | 73.34 | 73.95 |
| CDR | 63.72 | 63.22 |
| PES | 72.37 | 73.64 |
| MLC | 73.28 | 75.61 |
| CTRR | 72.71 | 73.68 |
| FPL | 73.54 | 73.57 |
| Meta-FPL | 73.61 | 73.94 |
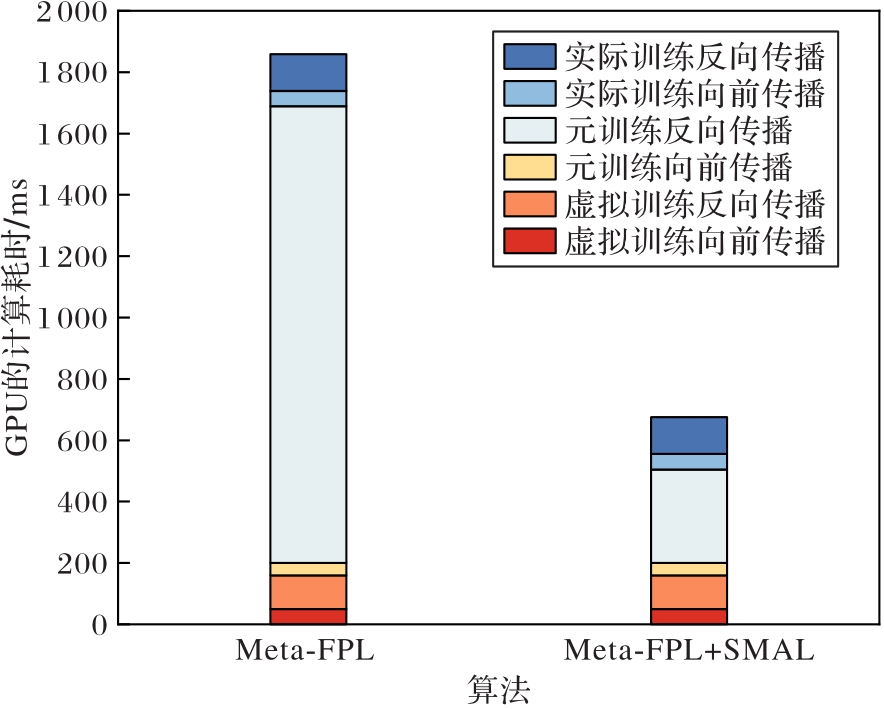
图6 Meta-FPL算法和Meta-FPL+SMAL算法训练时间影响的消融实验结果
Fig. 6 Ablation experiment results of influence of Meta-FPL algorithm and Meta-FPL+SMAL algorithm on training time
| [1] | JORDAN M I, MITCHELL T M. Machine learning: trends, perspectives, and prospects [J]. Science, 2015, 349(6245): 255-260. |
| [2] | WANG X, XIE D, ZHENG Y. Referring expression grounding by multi-context reasoning [J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2022, 160: 66-72. |
| [3] | KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks [J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. |
| [4] | GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation [C]// Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2014: 580-587. |
| [5] | LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 936-944. |
| [6] | CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs [J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4): 834-848. |
| [7] | HU G, HUA Y, YUAN Y, et al. Attribute-enhanced face recognition with neural tensor fusion networks [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 3764-3773. |
| [8] | LEE D H. Pseudo-label: the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [9] | 黄涵.基于深度学习的标签噪声学习算法综述[J].信息系统工程,2023(10): 39-42. |
| HUANG H. A review of label noise learning algorithms based on deep learning [J]. China CIO News, 2023(10): 39-42. | |
| [10] | FRÉNAY B, VERLEYSEN M. Classification in the presence of label noise: a survey [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(5): 845-869. |
| [11] | FRÉNAY B, KABÁN A. A comprehensive introduction to label noise [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [12] | ALGAN G, ULUSOY I. Image classification with deep learning in the presence of noisy labels: a survey [J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 215: No.106771. |
| [13] | ARPIT D, JASTRZĘBSKI S, BALLAS N, et al. A closer look at memorization in deep networks [C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2017: 233-242. |
| [14] | SONG H, KIM M, PARK D, et al. Learning from noisy labels with deep neural networks: a survey [J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(11): 8135-8153. |
| [15] | BARRON J T. General and adaptive robust loss function [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 4326-4334. |
| [16] | WANG Y, LIU W, MA X, et al. Iterative learning with open-set noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 8688-8696. |
| [17] | ZHANG Z, SABUNCU M R. Generalized cross entropy loss for training deep neural networks with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2018: 8792-8802. |
| [18] | WANG Y, MA X, CHEN Z, et al. Symmetric cross entropy for robust learning with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2019: 322-330. |
| [19] | FENG L, SHU S, LIN Z, et al. Can cross entropy loss be robust to label noise? [C]// Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conferences on Artificial Intelligence. California: ijcai.org, 2021: 2206-2212. |
| [20] | MA X, HUANG H, WANG Y, et al. Normalized loss functions for deep learning with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2020: 6543-6553. |
| [21] | SHU J, ZHAO Q, CHEN K, et al. Learning adaptive loss for robust learning with noisy labels [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [22] | DONG Y, LI J, WANG Z, et al. CoDC: accurate learning with noisy labels via disagreement and consistency [J]. Biomimetics, 2024, 9(2): No.92. |
| [23] | PATRINI G, ROZZA A, MENON A K, et al. Making deep neural networks robust to label noise: a loss correction approach [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 2233-2241. |
| [24] | XIA X, LIU T, WANG N, et al. Are anchor points really indispensable in label-noise learning? [C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 6838-6849. |
| [25] | WANG Z, HU G, HU Q. Training noise-robust deep neural networks via meta-learning [C]// Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2020: 4523-4532. |
| [26] | KANG B, XIE S, ROHRBACH M, et al. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [27] | LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection [C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 2999-3007. |
| [28] | HAN B, YAO Q, YU X, et al. Co-teaching: robust training of deep neural networks with extremely noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2018: 8536-8546. |
| [29] | SHU J, XIE Q, YI L, et al. Meta-weight-net: learning an explicit mapping for sample weighting [C]// Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2019: 1919-1930. |
| [30] | HU Z, YANG Z, HU X, et al. SimPLE: similar pseudo label exploitation for semi-supervised classification [C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 15094-15103. |
| [31] | KARIM N, RIZVE M N, RAHNAVARD N, et al. UNICON: combating label noise through uniform selection and contrastive learning [C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 9666-9676. |
| [32] | SONG H, KIM M, LEE J G. SELFIE: refurbishing unclean samples for robust deep learning [C]// Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: JMLR.org, 2019: 5907-5915. |
| [33] | PHAM H, DAI Z, XIE Q, et al. Meta pseudo labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2021: 11552-11563. |
| [34] | WU Y, SHU J, XIE Q, et al. Learning to purify noisy labels via meta soft label corrector [C]// Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021: 10388-10396. |
| [35] | ZHENG G, AWADALLAH A H, DUMAIS S. Meta label correction for noisy label learning [C]// Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021: 11053-11061. |
| [36] | WANG P, WANG X, WANG Z, et al. Learning accurate pseudo-labels via feature similarity in the presence of label noise [J]. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(7): No.2759. |
| [37] | PLEISS G, ZHANG T, ELENBERG E, et al. Identifying mislabeled data using the area under the margin ranking [C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2020: 17044-17056. |
| [38] | DENG L. The MNIST database of handwritten digit images for machine learning research [Best of the Web] [J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2012, 29(6): 141-142. |
| [39] | NETZER Y, WANG T, COATES A, et al. Reading digits in natural images with unsupervised feature learning [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [40] | KRIZHEVSKY A. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images [R/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [41] | TANAKA D, IKAMI D, YAMASAKI T, et al. Joint optimization framework for learning with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 5552-5560. |
| [42] | LARSEN J, NONBOE L, HINTZ-MADSEN M, et al. Design of robust neural network classifiers [C]// Proceedings of the 1998 International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing — Volume 2. Piscataway: IEEE, 1998: 1205-1208. |
| [43] | ZHAO G, LI G, QIN Y, et al. Centrality and consistency: two-stage clean samples identification for learning with instance-dependent noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2022 European Conference on Computer Vision, LNCS 13685. Cham: Springer, 2022: 21-37. |
| [44] | LIU S, NILES-WEED J, RAZAVIAN N, et al. Early-learning regularization prevents memorization of noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2020: 20331-20342. |
| [45] | XIA X, LIU T, HAN B, et al. Robust early-learning: hindering the memorization of noisy labels [EB/OL]. [2024-02-16]. . |
| [46] | BAI Y, YANG E, HAN B, et al. Understanding and improving early stopping for learning with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2021: 24392-24403. |
| [47] | YI L, LIU S, SHE Q, et al. On learning contrastive representations for learning with noisy labels [C]// Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2022: 16661-16670. |
| [48] | MILLER A C, FOTI N J, D’AMOUR A, et al. Reducing reparameterization gradient variance [C]// Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Red Hook: Curran Associates Inc., 2017: 3711-3721. |
| [1] | 王静, 刘嘉星, 宋婉莹, 薛嘉兴, 丁温欣. 基于空间变换网络和特征分布校准的小样本皮肤图像分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(8): 2720-2726. |
| [2] | 廖炎华, 鄢元霞, 潘文林. 基于YOLOv9的交通路口图像的多目标检测算法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(8): 2555-2565. |
| [3] | 彭鹏, 蔡子婷, 刘雯玲, 陈才华, 曾维, 黄宝来. 基于CNN和双向GRU混合孪生网络的语音情感识别方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(8): 2515-2521. |
| [4] | 张硕, 孙国凯, 庄园, 冯小雨, 王敬之. 面向区块链节点分析的eclipse攻击动态检测方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(8): 2428-2436. |
| [5] | 葛丽娜, 王明禹, 田蕾. 联邦学习的高效性研究综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(8): 2387-2398. |
| [6] | 张子墨, 赵雪专. 多尺度稀疏图引导的视觉图神经网络[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2188-2194. |
| [7] | 向尔康, 黄荣, 董爱华. 开放生成与特征优化的开集识别方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2195-2202. |
| [8] | 索晋贤, 张丽萍, 闫盛, 王东奇, 张雅雯. 可解释的深度知识追踪方法综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2043-2055. |
| [9] | 王震洲, 郭方方, 宿景芳, 苏鹤, 王建超. 面向智能巡检的视觉模型鲁棒性优化方法[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2361-2368. |
| [10] | 王慧斌, 胡展傲, 胡节, 徐袁伟, 文博. 基于分段注意力机制的时间序列预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2262-2268. |
| [11] | 赵小阳, 许新征, 李仲年. 物联网应用中的可解释人工智能研究综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(7): 2169-2179. |
| [12] | 花天辰, 马晓宁, 智慧. 基于浅层人工神经网络的可移植执行恶意软件静态检测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(6): 1911-1921. |
| [13] | 李岚皓, 严皓钧, 周号益, 孙庆赟, 李建欣. 基于神经网络的多尺度信息融合时间序列长期预测模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(6): 1776-1783. |
| [14] | 王向, 崔倩倩, 张晓明, 王建超, 王震洲, 宋佳霖. 改进ConvNeXt的无线胶囊内镜图像分类模型[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(6): 2016-2024. |
| [15] | 王文鹏, 秦寅畅, 师文轩. 工业缺陷检测无监督深度学习方法综述[J]. 《计算机应用》唯一官方网站, 2025, 45(5): 1658-1670. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||